Imagine having a powerful, clean energy source you can take anywhere. That’s the core idea behind portable natural gas tanks. These containers are engineered to safely hold natural gas, either as a compressed gas (CNG) or a super-chilled liquid (LNG), giving you a reliable power source for everything from a remote worksite to an emergency backup system for a hospital.
Unlocking Off-Grid Energy With Mobile Gas Solutions
Ever wonder how a major construction project gets gas power long before the utility lines are in? Or how a factory keeps running when its main gas pipeline is down for maintenance? This is where portable natural gas tanks come in. They act like a mobile pipeline, delivering clean energy right where it’s needed, exactly when it's needed.
Think of it like a giant power bank for industrial use. Instead of being tied to the grid or a permanent gas line, these tanks give you true energy independence. This kind of flexibility is a game-changer for industries working in remote locations or dealing with fluctuating energy needs. For instance, a new housing development can use temporary natural gas to fire up heating systems and secure occupancy permits, sidestepping what could be very expensive delays.
The Two Faces of Portable Natural Gas
At the heart of this technology are two different ways of storing natural gas. Each has its own properties and is better suited for different jobs. Getting a handle on their differences is the first step in picking the right one for your project.
- Compressed Natural Gas (CNG): This is natural gas squeezed into a tank at extremely high pressure. Think of packing a huge amount of air into a small, super-strong scuba tank. CNG is a fantastic choice for jobs where you need gas on and off or for shorter periods.
- Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG): This is natural gas that’s been cooled down to a mind-boggling -260°F (-162°C), which turns it into a liquid. This process shrinks its volume by more than 600 times. It’s like turning a room full of steam back into a single drop of water—an incredibly dense way to store energy, making it perfect for long-term or high-demand situations.
This basic difference—high pressure versus extreme cold—shapes everything from the tank’s design and materials to where it works best.
Why Mobile Natural Gas Matters
As more industries look for flexible and cleaner energy, portable natural gas has become more important than ever. These tanks act as a crucial bridge, letting businesses tap into the benefits of natural gas—which burns cleaner and is often cheaper than diesel or propane—without having to wait for permanent pipes to be laid.
By providing a temporary, on-demand supply, portable natural gas solutions prevent project interruptions, accelerate timelines, and ensure operational continuity. They represent a practical approach to energy logistics in a world that values both efficiency and environmental responsibility.
In this guide, we'll pull back the curtain on the technology behind these mobile energy solutions. We’ll break down CNG and LNG, look at how they’re used in the real world, and give you the essential knowledge you need to make smart decisions for your off-grid power needs.
Understanding CNG and LNG Tank Technologies
When you start looking into portable natural gas, you’ll quickly run into two main players: Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) and Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG). They both use the same fuel, but how they store it is night and day. Think of it like water—you can store it as high-pressure steam or as a solid block of ice. That fundamental difference in storage method shapes everything about the tank, from its design and energy capacity to what it’s best used for.
Compressed Natural Gas: Power Under Pressure
Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) is all about pressure. Imagine squeezing a massive amount of air into a small, incredibly tough balloon. That's essentially what a CNG tank does. The natural gas, still in its gaseous state, is compressed to a staggering 3,000 to 3,600 pounds per square inch (psi).
This kind of pressure demands a seriously robust container. CNG tanks are heavy-walled, cylindrical workhorses, typically built from steel or advanced composite materials to handle the stress. This straightforward, high-pressure approach makes CNG a fantastic choice for situations where you need fuel ready to go at a moment's notice, without a lot of complex handling.
As the world leans into cleaner energy, the CNG tank market has seen some serious growth. North America has been a major driver, holding a 36.5% revenue share thanks to its widespread use in natural gas vehicles (NGVs), tough emission standards, and a solid refueling infrastructure. In fact, on-board CNG tanks for vehicles captured a massive 72.4% market share, showing just how common they’ve become. You can dig deeper into these trends by checking out recent industry reports.
Liquefied Natural Gas: The Deep Freeze Approach
On the other end of the spectrum, Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) uses extreme cold to get the job done. If CNG is about pressure, LNG is about temperature. Picture turning an entire room filled with steam back into a single, tiny drop of water—that’s the core idea here. Natural gas is cryogenically chilled all the way down to -260°F (-162°C).
At that ridiculously cold temperature, the gas transforms into a liquid. This process shrinks its volume by over 600 times, packing an incredible amount of energy into a small space. Of course, storing something that cold requires a special kind of container. LNG tanks are basically high-tech thermoses, using vacuum insulation to maintain those frigid temperatures and handle the low-pressure liquid inside.
This amazing energy density makes LNG the go-to choice for heavy-duty jobs that burn a lot of fuel and can’t stop to refuel often.
It all boils down to one key difference: CNG uses immense pressure to store gas, while LNG uses intense cold to store liquid. This single fact dictates the tank's weight, its complexity, and just how much energy you can pack into it.
To see what this means in the real world, check out the infographic below. It breaks down how capacity, weight, and runtime stack up for different sizes of portable natural gas tanks.
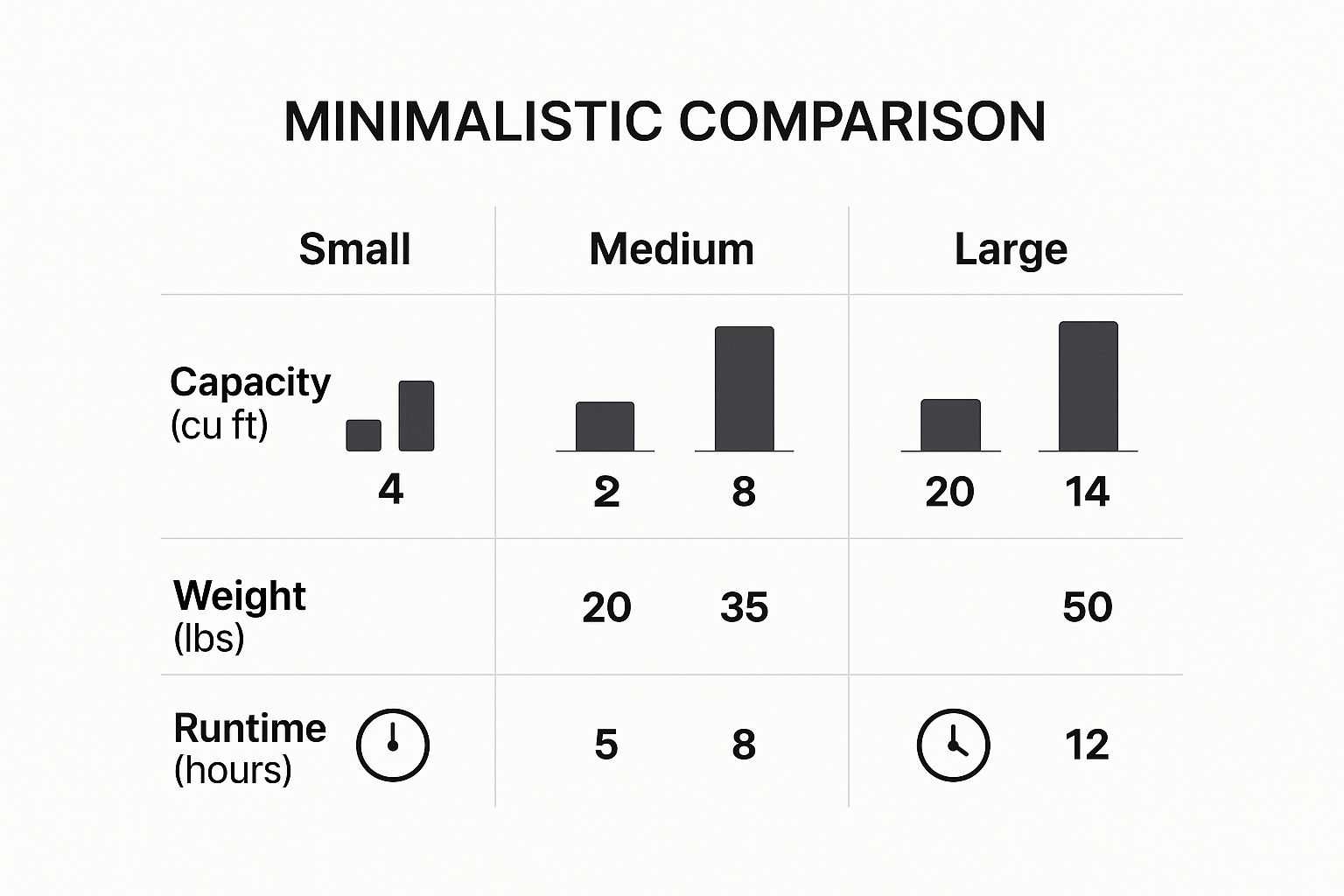
As you can see, bigger tanks mean significantly longer runtimes, which is why they’re perfect for powering continuous industrial operations.
Comparing CNG vs LNG Portable Tanks
So, how do you choose between CNG and LNG? It really comes down to understanding what each one brings to the table. One is simple and quick to deploy, while the other is an energy powerhouse built for the long haul.
This table provides a side-by-side comparison of the key characteristics of CNG and LNG tanks to help you quickly understand their fundamental differences.
| Feature | CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) | LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) |
|---|---|---|
| Storage State | High-pressure gas (3,000-3,600 psi) | Low-pressure, cryogenic liquid (-260°F) |
| Energy Density | Lower | Higher (approx. 2.4 times denser than CNG) |
| Tank Technology | Heavy, high-strength cylinders | Insulated, vacuum-sealed cryogenic tanks |
| Portability | Excellent for smaller, mobile applications | Better for large-scale, long-haul transport |
| Ideal Use Cases | Vehicle fleets, temporary industrial power, pipeline integrity testing | Marine shipping, long-haul trucking, remote power generation |
| Refueling Time | Relatively fast, similar to gasoline | Slower due to cryogenic handling requirements |
In the end, this isn't about which technology is "better." It’s about picking the right tool for the job. CNG is the star player for jobs that need flexibility and frequent use, like fueling a fleet of city buses. LNG, on the other hand, is the undisputed champ for powering a cargo ship across the ocean or keeping a remote mining operation running for weeks at a time.
How to Choose the Right Portable Gas Tank

Picking the right portable natural gas tank is more than just a technical choice—it's a strategic move that directly affects your project's efficiency, budget, and safety. You wouldn't use a screwdriver to do a sledgehammer's job, and the same logic applies here. You've got to match the tank to the task.
This means digging a little deeper than the surface-level specs. If you don't, you could end up with frequent, costly refills or, on the flip side, paying for way more capacity than you'll ever use. The sweet spot is finding that perfect balance between fuel volume, tank type, and how you’ll actually be using it.
Define Your Fuel Capacity Needs
First things first: how much gas do you really need? Answering this question is the bedrock of your entire decision. You need to get a solid estimate of your total energy consumption over a set period, whether that's a single day, a week, or the full length of a job.
Start by listing every piece of equipment that will be running on the gas. For each one, find its fuel consumption rate, which is usually measured in British Thermal Units (BTUs) or cubic feet per hour. Multiply that rate by how many hours you expect it to run each day, and you'll have a good baseline for your daily needs.
For instance, heating a massive commercial building during construction will demand a much higher volume of gas than simply commissioning a single backup generator. A good rule of thumb is to always add a 15-20% buffer to your final estimate. This covers you for unexpected demand or a sudden cold snap.
Getting this calculation right from the start helps you avoid the headache of running out of fuel mid-operation, keeping your project on track without costly interruptions.
Match the Tank to the Application
Once you've got your volume figured out, the next question is how you'll be using the fuel. Is this for a stationary setup, or will it be on the move? The answer will quickly point you toward the right solution, whether it's CNG or LNG, and the specific tank design that makes the most sense.
- Stationary Power: For jobs like providing temporary heat to a building or powering a fixed industrial process, large-volume CNG trailers or tube skids are often the best bet. They're relatively easy to set up and deliver a steady, reliable supply.
- Mobile Fueling: If you need to fuel vehicles like transit buses or refuse trucks, lightweight composite CNG tanks are the industry standard. Their lower weight is a huge deal, as it helps maximize the vehicle’s payload and overall fuel efficiency.
- Heavy-Duty & Long-Haul: When you're dealing with massive energy demands over long distances—think cargo ships or long-haul trucks—LNG is the undisputed champion. Its incredible energy density means you can store way more fuel in the same footprint, dramatically extending how far you can go between refills.
Thinking through the application narrows the field from a dizzying number of options to just the few that are truly a good fit for your project.
Consider Material and Construction
The material a tank is made from has a direct impact on its weight, durability, and price tag. This is a make-or-break factor, especially for mobile uses where every pound counts. Your main choices are steel and composite.
| Material Type | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy, incredibly tough, and budget-friendly. This is the old-school, workhorse option for stationary storage. | Stationary industrial sites, large-volume tube trailers, and any situation where weight isn't the top priority. |
| Composite | Super lightweight (up to 70% lighter than steel) and corrosion-resistant, but comes with a higher upfront cost and a defined service life. | On-board vehicle fuel tanks, mobile fueling rigs, and any application where being nimble and lightweight is essential. |
For example, a fleet of natural gas-powered delivery vans will almost certainly use lightweight composite CNG tanks to boost their mileage. On the other hand, a temporary gas supply for a manufacturing plant would probably be a durable, cost-effective steel tube trailer.
Prioritize Safety and Compliance
Safety isn't just a factor; it's the most important one. These tanks operate under extreme conditions—either immense pressure or cryogenic temperatures—so they absolutely must meet strict regulatory standards. There is no room for compromise here.
When looking at a tank or a service provider, always confirm that the equipment has the right certifications for your region and specific use case. The big ones to look for are:
- DOT (Department of Transportation): This is a must-have for any tanks being moved on public roads in the United States.
- ISO (International Organization for Standardization): These are global standards that speak to a product's quality, safety, and reliability.
Partnering with a trusted provider like Blue Gas Express takes the guesswork out of the equation. It guarantees that all equipment is meticulously maintained and fully compliant, giving you peace of mind and a safe, dependable energy source for your project.
Where Portable Natural Gas Really Shines

The theory is great, but the true value of portable natural gas tanks comes to life out in the field. They aren't just a niche product; they are incredibly versatile tools that solve real-world energy problems across dozens of industries. Think of them as the ultimate energy bridge, connecting a site’s immediate power needs with the grid that might be miles or months away.
Let's dig into a few common scenarios where these mobile energy units are making a massive difference, from keeping job sites running to powering critical services when the grid goes down.
Powering Remote Construction and Industrial Sites
Picture a sprawling construction project, miles from the nearest utility hookup. The traditional approach means waiting weeks, or even months, for a permanent gas line to be installed. That’s a project killer. This is exactly where portable natural gas tanks come in.
Large CNG tube trailers can be trucked directly to the site, providing an immediate and dependable fuel source for all sorts of power-hungry tasks:
- Temporary Heating: They can fire up massive industrial heaters for curing concrete, drying out materials, or just keeping the crew warm enough to work through a cold snap. This keeps the project on schedule, period.
- Heavy Machinery: Equipment like asphalt plants and large-scale generators can run on natural gas, which is often a cleaner and more cost-effective option than diesel.
- System Commissioning: You can test and fire up new boilers, furnaces, and other gas-powered equipment long before the utility company finishes its work.
This kind of on-demand energy helps builders get their occupancy permits sooner and dodge the steep financial penalties that come with project delays.
Keeping the Lights On During Emergencies and Outages
When a pipeline needs maintenance or a natural disaster strikes, some facilities simply can't afford to go dark. Hospitals, data centers, and critical manufacturing plants need a constant, uninterrupted flow of energy to operate safely.
In these high-stakes situations, portable natural gas tanks act as an essential lifeline. A mobile CNG or LNG unit can be brought in quickly to fuel backup generators, ensuring vital services never skip a beat. Unlike diesel that has to be stored on-site and can degrade, natural gas can be trucked in continuously for as long as needed.
This makes portable gas a non-negotiable part of any serious emergency preparedness or business continuity plan. It delivers clean, reliable backup power that can be scaled up or down to meet the demands of an unpredictable event.
Fueling a Cleaner Future in Transportation
The transportation industry is a massive energy user, and the push for cleaner emissions has put natural gas front and center. Portable tanks are a cornerstone of this shift, fueling everything from city buses to long-haul freight trucks.
- City Bus Fleets: Many cities are switching their bus fleets to run on cleaner CNG. Lightweight composite tanks are built right into the buses, and mobile fueling stations can be set up at depots for easy overnight refueling.
- Long-Haul Trucking: For trucks that cover serious mileage, LNG is the fuel of choice. Its incredible energy density means a much longer range between stops, making it a truly viable alternative to diesel for cross-country shipping.
- Marine Vessels: The shipping industry is also embracing LNG to comply with tough international emissions regulations. LNG is brought to ports by truck or barge to refuel massive ships, drastically cutting their environmental footprint.
This growing adoption is a big reason the global market for portable fuel tanks, including portable natural gas tanks, was recently valued at around USD 500 million. Experts see it growing at a CAGR of roughly 6%, thanks to surging demand in sectors like construction, marine, and agriculture where off-grid power is a necessity. You can dive deeper into these trends by checking out the portable fuel tank market research.
Safety First: Handling Portable Natural Gas the Right Way
Working with portable natural gas isn't something to take lightly. Whether it's high-pressure CNG or super-cooled LNG, these systems are built tough with plenty of safety features baked in. But at the end of the day, safe handling and sticking to the rules are what truly keep a job site secure.
Think of it like any other piece of powerful industrial equipment—you have to respect it to use it safely and effectively. The good news is that the safety protocols are straightforward and designed to stop problems before they start. Following these guidelines will give you and your crew the confidence to manage portable gas without a second thought.
Where You Put the Tank Matters
One of the biggest safety calls you'll make is deciding where to place a portable natural gas tank. The guiding principle is simple: keep it secure, give it breathing room, and place it far away from anything that could ignite the gas. This is less of a suggestion and more of a hard-and-fast rule.
Here’s what that looks like in practice:
- Find Solid Ground: The tank needs to sit on a firm, level surface. Uneven or soft ground is a no-go, as it could cause the unit to tip or shift unexpectedly.
- Let it Breathe: Always store tanks in a well-ventilated, open area. Natural gas is lighter than air, so if a small leak did happen, it would rise and scatter quickly. Never put it in an enclosed space like a shed, where gas could get trapped.
- Keep Your Distance: Position the tank a safe distance from buildings, air vents, and property lines. Most importantly, keep it well away from any potential ignition sources—that means no open flames, certain types of electrical gear, or designated smoking areas nearby.
Securing the tank is just as crucial. Make sure it’s stable and can't be bumped or knocked over, especially on a busy site with lots of moving parts.
The Right Way to Connect and Disconnect
Hooking up and disconnecting hoses might feel like a routine task, but it’s a moment that requires your full attention. Rushing these steps is just asking for trouble. Always stick to the specific procedures from your supplier, like Blue Gas Express, because they know their equipment best.
While the exact steps might differ slightly, the core process is always the same:
- Give Everything a Once-Over: Before you connect anything, do a quick visual check of the hoses, valves, and fittings. Look for cracks, wear, or any other damage. A bad hose is a major hazard and needs to be replaced immediately.
- Get a Good, Tight Seal: Make sure every fitting is seated correctly and tightened to the manufacturer's specs. Loose connections are one of the most common causes of leaks.
- Follow the Valve Sequence: There's a right order for opening and closing valves to safely bring the lines up to pressure and vent them down. Following that sequence prevents a sudden, uncontrolled release of gas.
Safety isn't a "set it and forget it" thing. It's an active process. If you treat every connection with methodical care, you can prevent simple, routine tasks from turning into accidents. Always double-check your work.
Daily Checks and What to Do in an Emergency
Regular inspections are your best defense against potential problems. You don't have to be a certified tech to spot the early warning signs that something's off. A quick walk-around at the start of each day can make all the difference.
Keep an eye out for these tell-tale signs:
- Physical Damage: Any new dents, deep scratches, or corrosion on the tank?
- Leaks or Icing: See any frost or ice forming on valves or fittings? That's a classic sign of a leak, especially with cryogenic LNG.
- Worn-Out Hoses: Check for cracks, bulges, or scuffs on the hoses.
- Pressure Readings: Do the gauges show a pressure reading within the normal operating range?
On the off chance you think you have a leak—you'll likely smell the distinct "rotten egg" odor they add to the gas for this very reason—you need to act fast. Get everyone out of the area immediately, shut down any potential ignition sources, and call your gas provider and emergency services from a safe distance.
The Future of Portable Natural Gas Technology

The world of portable natural gas isn't standing still. Driven by the constant need for better efficiency and rock-solid safety, the technology is moving well beyond the heavy steel cylinders of the past. We're seeing new designs that are lighter, tougher, and a whole lot smarter. This isn't just about minor tweaks—it’s a fundamental rethinking of what mobile energy can do.
A major part of this evolution is happening in materials science. Researchers are pushing the envelope with advanced composite materials, which combine tough polymers with high-strength fibers like carbon or glass. The result? Tanks that can be up to 70% lighter than traditional steel ones, all while maintaining their structural integrity. For any mobile application, that's a game-changer. It means better fuel economy for vehicles and far easier handling on job sites.
At the same time, LNG technology is taking huge strides. Innovations in cryogenic insulation now allow tanks to hold their super-cold temperatures for much longer, which drastically cuts down on the amount of gas lost to boil-off. This makes LNG an even more reliable and practical choice for long-term power in remote locations.
Smarter Tanks for a Smarter Grid
The next big step for portable natural gas tanks is all about brains. Imagine a tank that knows exactly how much fuel it's holding, keeps a constant watch on its internal pressure and temperature, and sends an alert straight to your phone when it's time for a top-up. That's not science fiction; it's happening right now.
By embedding smart sensors and IoT (Internet of Things) connectivity, these containers are evolving from simple vessels into intelligent, connected assets. This opens up a ton of practical benefits:
- Predictive Maintenance: The system can spot potential issues long before they turn into real problems.
- Optimized Logistics: With real-time data, fuel deliveries can be scheduled with pinpoint accuracy.
- Enhanced Safety: Instant alerts for any pressure or temperature deviations provide another crucial layer of protection.
This move toward data-driven management is all about boosting reliability and streamlining operations. It helps companies like Blue Gas Express deliver a more proactive and seamless service, giving clients peace of mind that they'll never be caught off guard by an empty tank.
Meeting the Demand for Cleaner Energy
Looking beyond the hardware, the broader energy market is also shaping the future of portable gas. As the world pivots toward cleaner energy, natural gas has emerged as a critical "bridge fuel." It burns much cleaner than diesel or coal, allowing industries to lower their carbon footprint without having to completely re-engineer their operations.
This shift is easy to see in the market numbers. Take the global market for LNG tank containers, a key segment of portable natural gas storage. It was valued at USD 0.15 billion and is on track to more than double, hitting a projected USD 0.33 billion at a 9% CAGR. This growth is a direct result of standardized designs and better materials. If you're interested in the details, you can find more on the LNG tank container market's expansion.
All these advancements are cementing portable natural gas as a vital part of our modern energy mix.
Got Questions About Portable Gas Tanks? We’ve Got Answers.
Even after getting the hang of the basics, you probably still have some practical questions about how these tanks fit into real-world scenarios. Let's tackle a few of the most common ones that come up.
How Far Can You Actually Go on One of These Tanks?
This is the big question for anyone considering natural gas for vehicles. The answer really depends on two things: the tank’s size and the vehicle's fuel efficiency. To keep things simple, the industry often talks in gasoline gallon equivalents (GGEs), so you can make a direct comparison.
For most cars and light trucks running on CNG, you can expect a driving range between 150 to over 300 miles. That’s right in line with a typical tank of gasoline. When you step up to heavy-duty trucks using LNG, the range gets a serious boost, often topping 700 miles on a single fill-up.
The bottom line? Modern natural gas vehicles have more than enough range for daily commutes and even long-haul trucking. They're a genuinely practical, cleaner alternative to gasoline or diesel.
Can I Use a Portable Natural Gas Tank for Home Backup Power?
In short, no. The large, high-pressure CNG tanks and super-cooled cryogenic LNG tanks you see in industrial settings are built for entirely different purposes. They're not designed, tested, or certified for residential use.
The safety protocols, specialized handling, and venting systems required for these tanks just aren't practical or safe for a home environment. For your house, it's best to stick with approved backup power solutions, like a standard propane or gasoline generator.
What's the Lifespan of a Portable Natural Gas Tank?
How long a tank lasts really comes down to what it’s made of and what it’s used for. Each type has its own service life and mandatory inspection schedule to keep things safe.
Here's a quick look at the typical timelines:
- Steel CNG Tanks: These are the rugged workhorses of the industry. With proper care and inspections, they can easily last 20 years or more.
- Composite CNG Tanks: While much lighter, these tanks have a fixed lifespan, usually around 15 to 20 years. Once they hit their expiration date, they have to be taken out of service for good.
- Cryogenic LNG Tanks: These are built for the long haul. They don't have a strict expiration date but require regular, thorough inspections to make sure their vacuum insulation and overall structure are holding up.
Need a temporary natural gas supply for your next big project? The team at Blue Gas Express delivers safe, scalable mobile CNG and LNG solutions directly to your construction or industrial site. Keep your project running without a hitch by visiting the Blue Gas Express website to get your energy needs covered.