Pipe line trucks, which we in the industry often call "mobile pipelines," are essentially self-contained, temporary natural gas connections on wheels. These specialized rigs haul either compressed or liquefied natural gas right where it's needed, serving as a lifeline when the main gas lines are down.
They are critical for ensuring energy continuity during pipeline maintenance, emergencies, or even construction delays. Think of it as an on-demand energy bridge that keeps the gas flowing.
Why Mobile Pipelines Are Mission Critical

Let's paint a picture. A hospital is hit with a major gas line failure during a brutal winter storm. Without gas, there's no heat, no hot water for sterilization—a genuine crisis. This is where a mobile pipeline truck rolls in, hooks up, and restores the gas supply, literally preventing a disaster.
These aren't just a "nice-to-have" backup. For modern energy infrastructure, they're an essential tool. They offer the flexibility to keep businesses, essential services, and entire communities online when something unexpected throws a wrench in the works. The goal is always a seamless, uninterrupted supply.
Preventing Costly Shutdowns and Delays
For a lot of businesses, if the gas stops, everything stops. Period. This is the reality for manufacturing plants, food processors, and large commercial buildings that depend on natural gas for heat, power, or specific production processes. An hour of downtime can mean tens of thousands in lost revenue.
A planned maintenance event shouldn't have to result in a complete operational shutdown. Mobile pipelines transform a potential week-long outage into a manageable, background task with zero downtime for the end-user.
Here’s another common scenario: a new subdivision is ready for homeowners, but the utility's permanent gas hookup is running weeks behind schedule. No gas means no occupancy permits. That’s a nightmare for the builder, who faces steep penalties and angry buyers. Deploying a temporary mobile pipeline gets the heat and appliances running, allowing families to move in on time.
The logistics of moving these massive units is a job in itself. Getting these rigs on-site efficiently often requires specialized haulage services to manage the transport and placement.
Understanding the Technology
The magic behind these trucks is their ability to pack a massive amount of natural gas into a relatively small space. This is done in one of two ways, and the right choice depends entirely on the job.
- Compressed Natural Gas (CNG): Here, natural gas is highly pressurized and stored in a series of durable cylinders on a trailer. CNG is the go-to for shorter projects or sites with more moderate energy needs. It’s quick to deploy and straightforward to manage.
- Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG): This is a bit more complex. The gas is cryogenically cooled to around -260°F (-162°C), which turns it into a liquid. The incredible part is that this process shrinks its volume by more than 600 times. LNG is the workhorse for long-term projects or large industrial users who need a huge, sustained energy supply from a single trailer.
No matter if it's CNG or LNG, each truck comes equipped with vaporization equipment. This gear carefully converts the stored gas back to its gaseous state at the precise pressure the customer’s system requires, perfectly mimicking the flow from a permanent pipeline.
Matching Your Needs with the Right Equipment

Let me be blunt: picking the wrong temporary gas setup is an expensive mistake. If you go too small, you're looking at service interruptions that defeat the whole purpose of bringing in a mobile unit. Go too large, and you're just burning money on capacity you’ll never touch. The first—and most critical—step is to get a crystal-clear picture of your operational needs.
This isn't about guesstimating. It's about doing the math before a single truck rolls onto your site. You need a solid understanding of your facility's gas consumption patterns to make a smart call.
Calculating Your Gas Demand
Before you can even think about what kind of pipeline truck you need, you have to know your numbers. It all boils down to two key metrics: gas volume and delivery pressure. These two figures will dictate the size and type of mobile pipeline system your project absolutely requires.
Your starting point is your own historical natural gas usage data. Dig into your daily and even hourly consumption records, and pay close attention to those peak demand periods. A common pitfall I’ve seen time and again is when folks plan based on average use, which completely ignores the spikes that can bring a system to its knees.
Think about a large apartment complex on a frigid winter morning. The heating systems and hot water heaters all fire up at once, creating a massive, short-term spike in gas demand. That peak load—not the daily average—is what you have to plan for.
You need to nail down these specifics:
- Maximum Hourly Flow Rate: Get this number in Standard Cubic Feet per Hour (SCFH) or British Thermal Units (BTU) per hour.
- Total Daily Volume: How much gas do you burn through in a full 24-hour cycle?
- Required Inlet Pressure: What pressure, in pounds per square inch (PSI), does your facility’s internal plumbing need to run properly?
With these figures in hand, you can have a meaningful conversation with a mobile pipeline provider like Blue Gas Express and get a solution that actually fits.
Pro Tip from the Field: I always tell clients to add a buffer of at least 15-20% to their peak demand calculations. An unexpected cold snap or a sudden change in operations can send your gas usage soaring. That little bit of contingency ensures you have the capacity to handle it without a single hiccup.
CNG Tube Trailers vs LNG Vaporization Units
Once your demand is calculated, it's time to choose your technology. The decision between Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) and Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) really hinges on your project's scale and how long it's going to last. Each has its own sweet spot.
CNG is stored at very high pressure inside a series of connected cylinders mounted on a trailer. It’s a fantastic choice for projects with moderate gas needs or shorter timelines—think a few hours to several days. The equipment is generally more straightforward, which allows for rapid deployment during emergencies or planned maintenance.
LNG, on the other hand, is natural gas that’s been chilled to a liquid, drastically shrinking its volume. This makes it incredibly energy-dense. A single LNG trailer can hold the same amount of energy as several CNG trailers, making it the go-to for large industrial facilities or long-haul projects that might last for weeks or even months.
To make the choice easier, let's break down how these two mobile pipeline technologies stack up.
Mobile Pipeline Technology Comparison
Choosing between CNG and LNG isn't just about volume; it's about the logistics of your entire project. This table gives you a quick side-by-side look to help you decide which technology is the better fit for your specific situation.
| Attribute | CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) | LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Short-term projects, emergencies, moderate demand | Long-term projects, high-volume industrial use |
| On-Site Footprint | Larger for high volumes (may require multiple trailers) | Smaller, as one trailer holds more energy |
| Energy Density | Lower | Very high (over 600x more compact than gaseous state) |
| Deployment Speed | Typically faster for initial setup | Can require more site prep for vaporization unit |
Getting this right from the start saves you from major logistical headaches down the road. For example, a manufacturing plant needing a continuous gas supply for a two-week pipeline replacement would find LNG far more practical, as it avoids the constant trailer swap-outs a CNG solution would demand. But for a restaurant that just needs a one-day gas supply during a utility line repair, the simplicity and speed of a CNG tube trailer is the perfect solution.
Navigating the Regulatory and Permitting Maze
Deploying a mobile pipeline isn't as simple as parking a trailer and hooking up a hose. You’re dealing with a complex web of federal, state, and local rules, and getting it wrong can lead to serious fines, project-killing delays, and major safety hazards.
Think of it this way: you need a passport for your temporary gas supply. Every agency, from the Department of Transportation (DOT) right down to the local fire marshal, needs to stamp its approval. Getting this right from the very beginning is the only way to ensure a smooth operation.
Understanding the Core Compliance Layers
The rules for mobile gas solutions are stacked in layers, and you have to peel back each one. At the top, you have the DOT, which has very strict regulations for transporting hazardous materials like CNG and LNG. These rules cover everything from driver qualifications and vehicle placards to specific safety protocols during transit.
Next, you dive into state and local fire codes. This is often where things get very hands-on. The local Fire Marshal’s top priority is public safety, so they'll be looking closely at where you place the unit, how far it is from buildings and property lines, and what kind of emergency shutdown procedures you have in place.
Finally, you’ll almost certainly need permits from the city or county for temporary equipment placement. This is to make sure the truck isn’t breaking any zoning laws, blocking a right-of-way, or otherwise creating a public nuisance.
A Real-World Permitting Scenario
Let's say your project is a new commercial building that happens to be just 200 feet from a protected wetland. That single detail changes everything and ramps up the regulatory scrutiny big time. A standard permit application just won't cut it.
In a case like this, you can expect regulators to demand:
- An Environmental Impact Statement: A formal document explaining how you’ll prevent any potential gas leaks from damaging the sensitive ecosystem.
- A Detailed Spill Contingency Plan: This outlines the exact steps and equipment you have on-site to immediately contain and manage an incident.
- Enhanced Site Security Measures: Fencing, monitoring, and other protocols to keep unauthorized people away from the equipment, especially since it's near a public area.
For a project with this kind of complexity, you need to be talking to regulators months ahead of time. I’ve personally seen projects get stuck for weeks because the team underestimated the process and waited until the last minute to start the conversation.
My best advice is to treat regulators as partners, not obstacles. Go to them early with a solid plan, be completely transparent about what you’re doing, and show them you’ve thought through all the safety measures. A proactive, cooperative attitude can turn what feels like an adversarial process into a collaborative one.
The Critical Role of Transportation and Insurance
Just getting these units from point A to point B is a massive undertaking governed by its own set of rules. The U.S. trucking industry is the backbone of domestic freight, handling an incredible 72.7% of all tonnage moved. With the American Trucking Associations projecting freight volumes to hit nearly 14 billion tons by 2035, the need for compliant transport is only growing. Discover more about these freight projections and their impact on the industry.
Before a single tire hits the pavement, you have to sort out your insurance. Carefully decoding commercial vehicle insurance requirements is an absolute must for full legal compliance.
This isn't just a recommendation; proper insurance is a mandatory shield against liability and a core requirement for getting your operating permits. You need to ensure your provider offers comprehensive coverage that meets all federal and local minimums. Overlooking this can expose your entire operation to crippling financial and legal risk. This one piece of paperwork can make or break your project before it even starts.
Preparing Your Site for a Seamless Connection
You've picked the right equipment and have the permits in hand. Now, the real work begins on-site. Getting your location ready is where the plan meets the pavement, and a successful temporary gas deployment depends entirely on how well you prepare the ground.
Think of it as laying the foundation for a house. If the prep work is sloppy, everything that follows will be inefficient and, frankly, unsafe. This isn't just about clearing a patch of dirt; it's a methodical process that ensures a smooth, secure hookup from the mobile unit to your existing system.
Establishing a Solid Staging Area
First things first: you need to create a stable, secure home for the CNG or LNG trailer. These are incredibly heavy pieces of equipment, and the ground has to handle that weight without shifting or settling. Soft, muddy, or uneven ground is an absolute non-starter.
You’ll need to establish a firm, level pad. For most projects, this means paying attention to a few key details:
- A Solid Base: A well-compacted gravel pad or an existing asphalt lot usually does the trick. It needs to be rock-solid.
- Enough Elbow Room: The pad has to be big enough for the entire trailer, plus plenty of working room for the technicians. A typical CNG tube trailer can stretch over 50 feet long, so you can't just squeeze it in.
- Clear In-and-Out Access: Can a massive truck actually get to the spot? The path needs to be free of obstructions, with wide turning radii and no low-hanging power lines or branches.
This last point about accessibility is often overlooked but can derail a project quickly. The logistics of maneuvering these large vehicles are a major consideration. In fact, the market for Class 8 trucks—the heavy-duty workhorses used by pipe line trucking companies—is a good indicator of broader economic trends. Recent data showed net orders for these trucks hitting their lowest point since 2019, which suggests a more cautious investment climate among fleets. You can dig into the specifics in this trucking industry forecast.
The Technical Hookup Process
Once the trailer is safely parked, the real technical work begins. This is a precise operation handled only by certified technicians from your mobile gas provider. Their entire job is to safely integrate the high-pressure gas from the trailer into your facility’s lower-pressure system.
The hookup itself involves connecting specialized, high-pressure hoses from the trailer to a regulation station. This station is the heart of the operation. It takes that highly pressurized gas and methodically steps it down to the exact PSI your system needs to run. It's a delicate balancing act to maintain a perfectly consistent and reliable flow.
This infographic gives a great high-level overview of the approval process that happens long before a truck even arrives on-site.
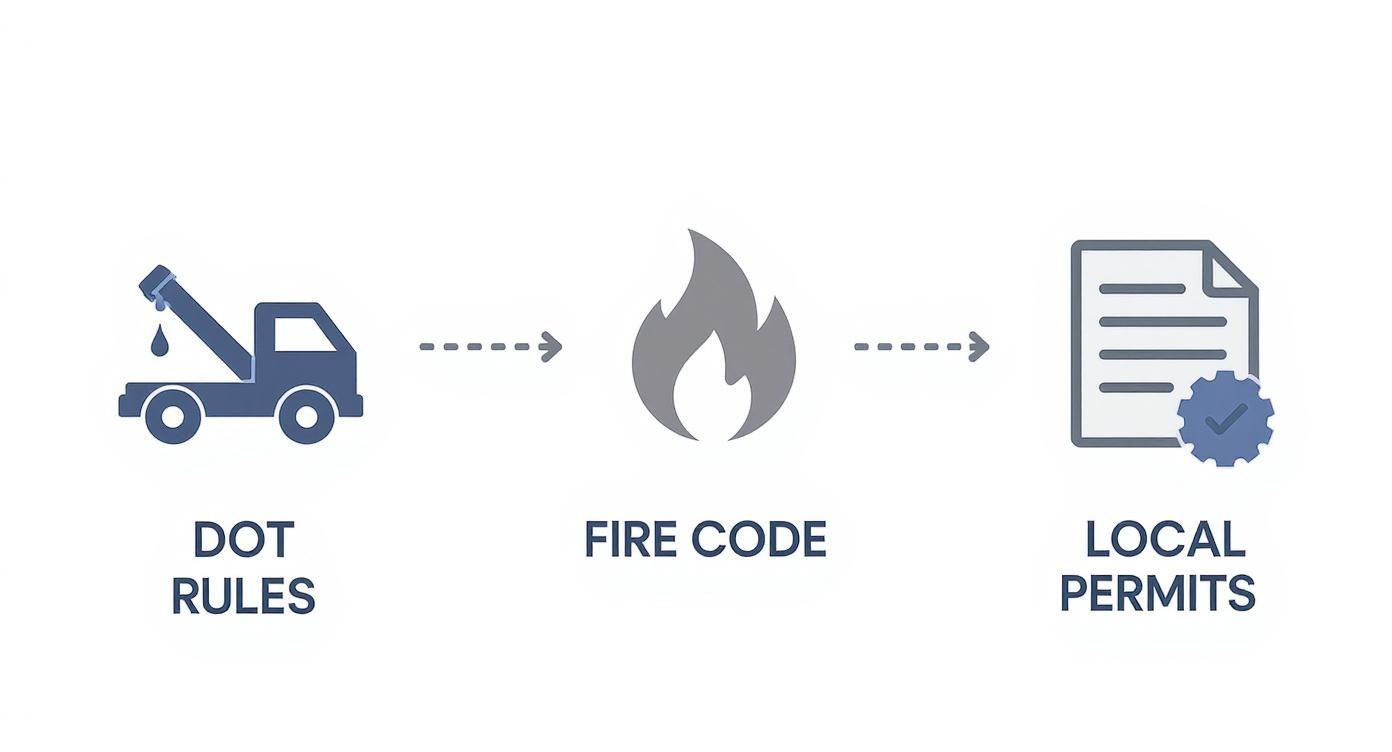
As you can see, the process flows from federal transport regulations down to local fire and equipment permits, with each layer of compliance building on the last.
Overcoming Site Constraints: A Real-World Example
Of course, not every site is a wide-open, perfectly level field. We recently managed a project for a downtown hospital in a cramped urban area. The only available space was a small, enclosed service alley with limited overhead clearance and constant pedestrian traffic just a few yards away.
In tight spaces, safety isn't just a protocol—it's an active, minute-by-minute process. The goal is to isolate the operation so effectively that the public doesn't even know it's happening.
Here’s how our team tackled it:
- Precision Placement: We chose a smaller, more maneuverable CNG truck. With a spotter team guiding him, a highly skilled driver carefully backed the unit into the tight alley with just inches to spare.
- Public Safety Barriers: The entire service alley was blocked off with hard barriers and clear signage. This created a completely secure work zone, isolated from any foot traffic.
- Continuous Monitoring: We stationed a technician on-site 24/7. Armed with handheld gas detectors, their sole job was to continuously monitor the connection points and surrounding area, ensuring any potential issue would be caught instantly.
This scenario proves that even the most difficult logistical challenges can be handled with meticulous planning and an absolute focus on safety. What could have been a logistical nightmare turned into a smooth, incident-free operation.
Getting Safety and Testing Absolutely Right

When you're dealing with mobile natural gas, there's simply no room for error. Safety isn't just a box to check—it's the bedrock of the entire operation. Every single valve, hose, and connection is a critical component, and that’s why we live by a strict set of testing protocols before, during, and after every job.
The moment our pipe line trucks pull up to your site, the real work begins. Long before any gas starts flowing, our technicians are already running through a comprehensive pre-operation checklist. This isn't just a quick walk-around; it's a deep dive meant to catch any potential issue, no matter how small.
Pre-Flow Integrity Checks
The first order of business is always leak detection. Technicians go over every connection point with a fine-tooth comb, from the trailer manifold to the final tie-in at your facility. We use a combination of tried-and-true methods and modern tech to guarantee a perfectly sealed system.
- The Soap Test: It might sound old-school, but it’s incredibly effective. A soapy water solution is brushed onto every fitting. If bubbles appear, you've found a leak that needs to be fixed on the spot.
- Electronic Gas Sniffing: To back up the visual check, technicians use handheld electronic gas detectors. These sensitive "sniffers" can detect tiny, invisible traces of gas, giving us that final confirmation that everything is 100% tight.
Only when every connection passes both tests without a single issue do we move on to the next phase.
Pressure Testing and System Verification
Once we've confirmed the system is sealed, we put it to the test under pressure. A technician will slowly introduce pressure into the lines and let it sit, keeping a close eye on the gauges. If the needle doesn't move, we know the connections are solid and can handle the full operational load.
This is also the point where we verify all the emergency shutdown (ESD) systems. These are the critical fail-safes designed to instantly stop the flow of gas if something goes wrong. We physically trigger these systems to make sure they're armed and ready to react in a split second.
A true safety culture isn't just about following a checklist. It's a mindset that treats that checklist as the absolute bare minimum. Every step is done with the full understanding that the safety of the crew and the public depends on it.
Continuous On-Site Monitoring
Getting the gas flowing doesn't mean the job is done. A trained technician stays on-site for the entire duration of the project, providing around-the-clock monitoring. Their only job is to watch over the equipment and ensure a safe, steady supply of gas.
This constant oversight is non-negotiable. It allows for an immediate response to any fluctuation in pressure, flow rates, or even changing weather conditions, providing an essential layer of security for the entire operation.
Speaking of logistics, getting heavy equipment to these project sites is a major undertaking. Flatbed trucks are the workhorses for hauling pipes and other oversized gear, and their availability is often a bellwether for the health of major infrastructure projects. As utility and energy work keeps freight volumes up, demand for this specialized transport stays hot in key markets. For more on this, you can check out the latest market analysis on flatbed freight trends and capacity at bm2freight.com. It’s a good reminder of the complex logistical web that supports these critical energy projects.
Got Questions About Temporary Pipeline Trucks? We've Got Answers.
When you're looking at bringing in a temporary gas solution, you’re bound to have questions. And you should. Getting the details right upfront is the difference between a smooth project and a costly headache. Let's walk through some of the most common things people ask when considering pipe line trucks.
This isn't just about the equipment; it's about the real-world logistics, timing, and responsibilities that make or break a project.
What’s the Real Cost of Renting a Mobile Pipeline?
There's no single price tag for renting a mobile pipeline—it really depends on the job. The final cost is a mix of a few key things: the type of gas you need (CNG vs. LNG), how much you'll use, and how long you'll need it on-site.
Generally, you can expect the costs to be broken down like this:
- The Gear: You'll have a daily or weekly rental fee for the trailer and all the regulation hardware that comes with it.
- The Gas Itself: You pay for what you use. This is usually measured per MCF (thousand cubic feet) or MMBtu (million British thermal units).
- Getting It There and Back: There are always mobilization and demobilization fees to cover the logistics of transporting the entire setup to your location and taking it away when you're done.
A smaller, quick job might be in the thousands, but a major industrial bypass lasting weeks can easily run into the hundreds of thousands. My advice? Always demand a detailed, itemized quote so you know exactly where your money is going.
How Quickly Can You Get a Unit Deployed?
The timeline for getting a mobile pipeline up and running can be anything from a few hours to several weeks. The biggest factor is whether we're talking about a planned project or a middle-of-the-night emergency.
For our existing partners who have sites pre-vetted and permits squared away, we can often have a truck on location and flowing gas within just a few hours. That kind of speed is absolutely essential when you’re dealing with an unexpected pipeline failure and every minute of downtime costs you.
But for a new project, the permitting process is almost always the longest part of the journey. Depending on the local rules and the project’s complexity, getting all the necessary approvals can take anywhere from one to four weeks.
This is why I can't stress this enough: start the planning and permitting conversation as early as you possibly can. Getting ahead of the regulatory side is the single best thing you can do to keep your project on track.
Who Actually Runs the Equipment On-Site?
This is a big one for safety and liability. The mobile pipeline provider—that's us—is responsible for operating and monitoring the equipment once it's on your property. This isn't something we hand off.
Our technicians are highly trained to manage the entire process. They handle everything from safely offloading the gas to dialing in the right pressure and keeping a close watch on all the hardware.
This setup ensures that certified experts are managing the technical side and all the safety protocols. Your crew will coordinate with our team and the local utility, of course, but they won't be asked to touch the mobile pipeline equipment. It’s a clear division of labor that keeps the operation safe, efficient, and compliant from start to finish.
At Blue Gas Express, our entire business is built on providing reliable, on-demand mobile gas solutions to keep your operations running without a hitch. If you're planning a project or facing a sudden interruption, we’re here to help.
Find out more about our CNG and LNG services at the Blue Gas Express website.