When you hear "pipeline," you probably picture a massive, underground network of steel pipes stretching for miles. But what if you could deliver natural gas without building a single foot of that infrastructure? That's the core idea behind a natural gas virtual pipeline.
Think of it as a 'pipeline on wheels.' Instead of a fixed physical line, it’s a sophisticated logistics system using trucks, trains, or ships to move natural gas wherever it's needed. This creates a flexible, scalable energy solution, especially for places cut off from the traditional gas grid.
Unlocking Energy Beyond the Grid

Picture a new manufacturing plant or a growing town that’s miles from the nearest gas main. Extending a traditional pipeline is a monumental project, often costing millions per mile and bogged down by years of planning and construction. This is exactly the kind of problem a virtual pipeline is built to solve.
This innovative approach isn't a single piece of equipment but a full-blown supply chain designed to make natural gas portable and bridge that energy gap.
The Core Concept of Portability
The science behind it all is pretty simple. In its natural state, gas takes up a huge amount of space, making it impractical to haul around. The key is to shrink its volume dramatically, which is done in one of two ways:
- Compressed Natural Gas (CNG): The gas is pressurized until it takes up less than 1% of its original volume. It stays a gas but is stored in super-strong, reinforced cylinders for transport.
- Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG): The gas is chilled to a frigid -260°F (-162°C), which turns it into a clear, non-toxic liquid. This amazing process shrinks its volume by 600 times, creating an incredibly dense energy source that's perfect for shipping over long distances.
Once compressed or liquefied, the gas is loaded onto specially designed trucks, railcars, or marine vessels for delivery. When it arrives at its destination, regasification equipment is on-site to turn it back into usable gas, ready to power homes and businesses.
A virtual pipeline offers the dependability of a traditional pipeline but with the unmatched flexibility of on-demand delivery. It's a mobile energy solution that brings power to places that would otherwise be left in the dark.
Meeting a Growing Global Need
This isn't just a niche concept; it's a rapidly expanding market solving real-world energy challenges. The demand for virtual pipelines is booming. The market was recently valued at $1.81 billion, up from $1.7 billion the previous year—a growth rate of about 6.6%. Projections show it climbing to $2.31 billion soon, maintaining a steady compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 6.3%. You can explore more virtual pipeline market insights on Market Report Analytics.
This growth isn't surprising. It shows just how effective these systems are at powering off-grid industries, fueling vehicle fleets, and even providing emergency gas during outages. By creating a natural gas virtual pipeline, companies can bypass the immense costs and geographical limitations of conventional infrastructure and ensure a reliable energy supply just about anywhere.
How the Virtual Pipeline Journey Unfolds
To really get a feel for a natural gas virtual pipeline, let's trace the path of a single molecule from the wellhead to the end user. This isn't just a simple case of filling up a truck and hitting the road. It's a highly coordinated process that turns a raw resource into a portable, on-demand energy source.
The whole system works by making natural gas compact enough to move around without a physical pipe. It all starts at the source, where gas is extracted and cleaned up. From there, it's sent to a specialized facility for the most important step: transformation. This is where the gas is either compressed into CNG or super-chilled into LNG, getting it ready for its journey.
Stage 1: Transformation for Transport
The first big step is to drastically shrink the volume of the gas. The choice of how to do this really depends on how far the gas needs to go and how much energy the customer needs.
- Compression (CNG): Here, the gas is pressurized to between 3,000 and 3,600 psi. It stays a gas, but it's squeezed into a much smaller space, perfect for filling high-strength cylinders. This approach is great for shorter distances and when you don't need massive volumes.
- Liquefaction (LNG): This method is a bit more dramatic. The gas is cooled down to a frosty -260°F (-162°C), which turns it into a liquid. The payoff? Its volume shrinks by a factor of 600. This incredible density makes LNG the go-to choice for moving huge amounts of energy over long hauls.
Deciding between CNG and LNG is a crucial fork in the road. It determines the kind of trucks, storage tanks, and handling procedures needed for the rest of the trip.
Stage 2: Loading and Mobile Delivery
Once the gas is either compressed or liquefied, it's ready to hit the road. It's carefully loaded into specially designed transport modules. For CNG, this usually means filling up a "tube trailer," which is essentially a truck pulling a series of interconnected high-pressure cylinders.
For LNG, the process involves pumping the cryogenic liquid into a certified ISO tank. You can think of these containers as giant thermoses on wheels. They have a double-walled, vacuum-insulated design to keep the LNG stable at its ultra-low temperature for the entire trip.
With the gas secure, the "pipeline on wheels" is officially on the move. Trucks, trains, or even ships carry these containers across hundreds of miles, navigating everything from major highways to remote access roads to reach places far off the traditional pipeline grid.
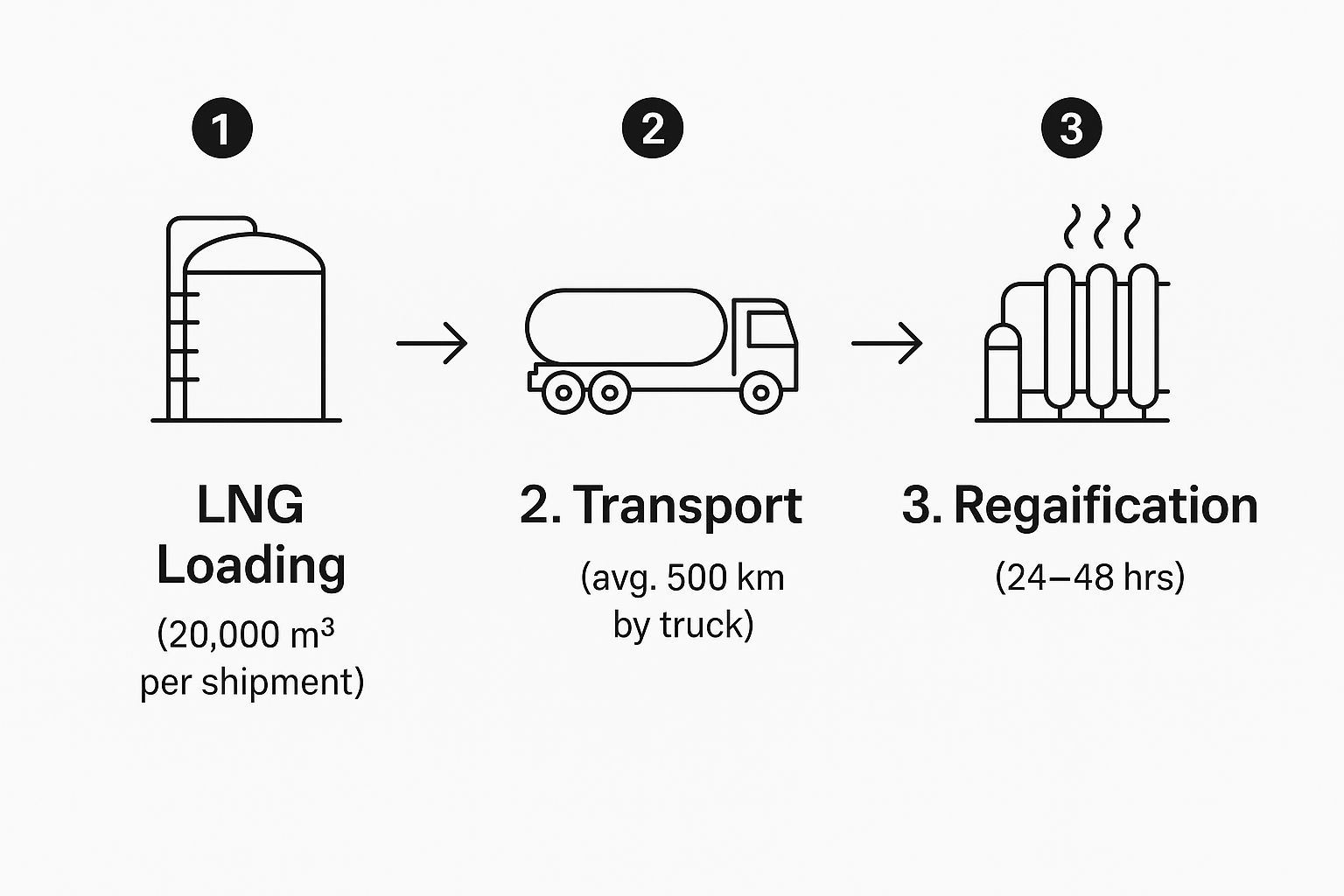
This visual gives you a great sense of the logistics involved. It shows how a large volume of LNG can be loaded, transported over a significant distance, and readied for use, all within a couple of days.
CNG vs. LNG in Virtual Pipelines
Choosing between CNG and LNG isn't just about temperature; it’s a strategic decision based on volume, distance, and cost. Each has its own strengths that make it better suited for different applications. The table below breaks down the key differences to help clarify when you might choose one over the other.
| Attribute | Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) | Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) |
|---|---|---|
| State | Gaseous, under high pressure | Liquid, at cryogenic temperatures |
| Energy Density | Lower | Much higher (600x denser than gas) |
| Storage | High-pressure cylinders (tube trailers) | Insulated cryogenic tanks (ISO tanks) |
| Ideal Distance | Shorter hauls (typically < 200 miles) | Long distances (200+ miles) |
| Capital Cost | Lower initial investment for facilities | Higher initial investment for liquefaction |
| Best For | Lower-volume, regional customers; fleet fueling | High-volume industrial users; remote power generation |
In short, CNG is often the more economical and practical choice for regional supply, while LNG's incredible energy density makes it the undisputed champion for long-distance, high-volume energy delivery.
Stage 3: Unloading and Regasification
The final leg of the journey happens right at the customer's site. When the truck arrives, the mobile storage unit is hooked up to on-site equipment, and the process of turning it back into usable energy begins. It's a safe, efficient operation designed for minimal disruption.
The critical step here is regasification, especially for LNG. This involves gently warming the liquid to turn it back into a gas. This is usually done with an ambient air vaporizer, a clever piece of equipment that uses the surrounding air temperature to do the heating—no external power needed.
Regasification is the magic that unlocks the energy stored in LNG. It seamlessly converts the dense liquid back into pipeline-quality gas, ready to power equipment, heat buildings, or run industrial processes.
Once it's a gas again, the natural gas is fed into the customer’s on-site piping at just the right pressure and flow rate. The result is a steady, reliable energy supply that’s identical to what you’d get from a physical pipeline. And just like that, a molecule that started deep underground has completed its natural gas virtual pipeline journey, delivering clean energy with incredible precision and flexibility.
The Technology Driving Virtual Pipelines
A virtual pipeline for natural gas isn't just a clever logistical trick; it's a carefully orchestrated system where rugged hardware and smart software work together. Every single step, from prepping the gas for its trip to making sure it arrives safely, relies on specialized technology. Without these critical pieces, the whole "pipeline on wheels" concept would fall flat.

The entire operation depends on advanced equipment built to handle natural gas under some pretty extreme conditions. This includes everything from the massive industrial plants that compress or liquefy the gas to the purpose-built containers that haul it. It’s these physical assets that form the tough, reliable backbone of the virtual pipeline.
The Hardware Foundation
At the core of any natural gas virtual pipeline is the hardware that makes it all possible. This isn't your average equipment; it's engineered for maximum safety, durability, and efficiency to keep the gas stable from the source all the way to the end user.
The journey starts at a processing plant, where powerful compressors or sophisticated cryogenic systems get the gas ready. From there, it's loaded into highly specialized transport modules.
CNG Tube Trailers: For Compressed Natural Gas (CNG), the go-to solution is a tube trailer. Think of a semi-trailer loaded with a bundle of huge, interconnected cylinders built from high-strength steel or composite materials. These are designed to hold gas under immense pressure—up to 3,600 psi—creating a safe, mobile storage unit.
LNG Cryogenic Tanks: Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) is a different beast entirely. The main challenge is keeping it incredibly cold. This calls for ISO-certified cryogenic tanks, which are basically giant, industrial-strength thermoses. They use a double-walled design with a vacuum seal in between to stop heat from getting in, keeping the LNG at a stable -260°F for the long haul.
These heavy-duty transport units are the true workhorses of the virtual pipeline, built to handle the bumps and rattles of road, rail, or sea travel while keeping their precious cargo secure.
The Digital Intelligence Layer
If the hardware is the body, then the software is the brain. A modern virtual pipeline operation is run by a smart digital layer that fine-tunes every part of the supply chain. This is what brings precision, boosts safety, and squeezes every bit of efficiency out of the process.
This digital oversight acts like a central nervous system, connecting every truck, tank, and sensor into one cohesive network. It gives operators a real-time view of everything, allowing them to make smart decisions, predict demand, and react instantly to anything that comes up.
The integration of digital tools transforms a simple delivery service into a dynamic, intelligent energy network. It ensures that the right amount of gas gets to the right place at the right time, safely and cost-effectively.
This digital ecosystem really boils down to two key components working in tandem:
IoT Sensors and Monitoring: Every single transport vessel is wired with a suite of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors. These little devices are constantly sending back vital data—internal pressure, temperature, volume levels, and exact GPS coordinates. This constant stream of information means someone is always watching, and any reading that falls out of the normal range triggers an immediate alert.
Logistics and Scheduling Software: All that data from the sensors flows into a central logistics platform. This software uses smart algorithms to map out the best delivery routes, schedule trucks, and manage the entire fleet. It can factor in real-time traffic, weather forecasts, and even how fast a customer is using gas to create a truly seamless supply chain.
And the technology isn't standing still. We're seeing exciting progress in cryogenic tech, the use of blockchain for tracking transactions, and even hybrid systems that combine LNG with renewable energy. You can get a deeper look into the future of LNG virtual pipeline technology and its market analysis on TBRC's blog. This constant innovation is what keeps the natural gas virtual pipeline a reliable and forward-thinking solution for energy delivery.
Why Go with a Virtual Pipeline?
So, why are so many industries and communities turning to natural gas virtual pipelines instead of waiting for the traditional kind? It really comes down to a powerful mix of financial, environmental, and practical benefits that make this model a seriously smart alternative. It completely changes the game for how businesses and utilities think about getting reliable energy.
Instead of staring down the barrel of a massive, multi-year construction project, you can tap into a flexible, on-demand energy supply. This approach lets you sidestep the huge upfront costs, endless construction timelines, and geographical headaches of physical pipelines, delivering clean energy right where you need it, when you need it.
Let's break down the core advantages driving this shift.
It's a Smarter Financial Move
The most obvious win is the money you save. Laying a conventional natural gas pipeline is an incredibly expensive and slow process. We're talking millions of dollars per mile and years of work before it's even operational. A virtual pipeline completely erases that massive initial investment.
You don't have to budget for acquiring land rights, digging trenches, or welding and burying miles of steel. The cost shifts to a much more predictable and manageable operational expense tied to logistics and service. This financial agility gives you a huge leg up:
- Dodge massive upfront costs: Keep your capital working for you in your core business instead of sinking it into a long-term infrastructure project.
- Match supply to demand: You only pay for the energy you actually need, avoiding the cost of building excess capacity that just sits there.
- Get up and running faster: Launch your operations and start generating revenue much sooner by sidestepping years of construction and regulatory approvals.
This is a game-changer for new industrial parks, growing manufacturing plants, or even residential developers who need gas service on a tight schedule to get buildings occupied.
A Clearer Path to a Cleaner Footprint
Beyond the bottom line, the natural gas virtual pipeline is a big step forward for environmental responsibility. By making cleaner-burning natural gas accessible, it helps users move away from dirtier, more carbon-heavy fuels like diesel, heating oil, or coal.
Natural gas burns much cleaner, producing far lower emissions of nasty pollutants like carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter. Making the switch means cleaner air and a smaller carbon footprint. For instance, a factory that swaps its diesel generators for natural gas can cut its CO2 emissions by roughly 27%.
A virtual pipeline is essentially a bridge to a cleaner energy future. It gives industries and communities a practical, immediate way to hit their emissions reduction targets without waiting years for a physical pipeline to be built.
This approach is particularly effective for remote operations, like mines or large farms, which have often been stuck using dirtier fuels simply because there was no other choice.
Unbeatable Flexibility in the Real World
Perhaps the most powerful advantage is the incredible agility a virtual pipeline offers. A traditional pipeline is permanent and fixed in place, but a mobile energy solution can adapt to almost any situation you can throw at it.
This "pipeline on wheels" can be rolled out quickly to meet temporary needs, respond to an emergency, or just provide extra fuel when demand spikes. Think about these scenarios:
- Temporary Supply: Powering heaters and equipment on a large construction site long before the permanent gas lines are connected.
- Emergency Response: Rapidly restoring gas service to a hospital or a neighborhood after a storm or a pipeline incident.
- Peak Shaving: Supporting the main grid during a winter cold snap when everyone cranks up the heat, preventing brownouts or service interruptions.
This adaptability guarantees a steady, reliable energy supply, no matter what's happening on the ground. For businesses like the ones served by Blue Gas Express, it means projects stay on schedule without costly delays, keeping everything running smoothly.
Virtual Pipelines in Action Across Industries
This is where the idea of a natural gas virtual pipeline stops being a concept and starts solving real-world energy problems. Its incredible flexibility makes it the go-to solution for all sorts of industries that are either off the grid or need a fast, temporary, or backup energy source. Think of it as a "pipeline on wheels," delivering clean and reliable energy right where it's needed, when it's needed.
From firing up remote industrial sites to making sure homes stay warm during a winter cold snap, virtual pipelines are proving their worth time and again. They offer a practical, efficient, and often cheaper way to fill energy gaps that would otherwise stop a project cold or interrupt essential services.

Fueling Off-Grid Industrial Operations
Let's face it, many of our most important industries—mining, manufacturing, agriculture—are located miles from the nearest city or established gas grid. For them, a virtual pipeline isn't just a nice-to-have; it's an economic lifeline.
Imagine a new factory being built in a rural industrial park. The wait for a physical pipeline extension could stretch on for years, burning through millions in potential revenue. A natural gas virtual pipeline, on the other hand, can be set up in just a few days. It provides the steady, powerful energy needed for heavy machinery and processing, getting the plant up and running right on schedule.
This speed to market is a massive competitive advantage. For example:
- Remote Mining: It can provide nonstop power for heavy equipment way out in the wilderness, slashing both fuel costs and emissions compared to the old diesel generators.
- Agricultural Facilities: It's perfect for fueling massive grain dryers or heating greenhouses in farming regions, making operations more efficient and less dependent on expensive propane.
Powering Vehicle Fleets
Companies and cities everywhere are looking to switch their vehicle fleets to cleaner fuels. Both CNG and LNG are fantastic, lower-emission alternatives to diesel for everything from heavy-duty trucks to city buses. Virtual pipelines are a key piece of the puzzle in making this switch happen.
Instead of sinking a ton of money into a permanent fueling station tied to a main gas line, a mobile CNG or LNG delivery system can set up a fueling point just about anywhere. An entire fleet of delivery trucks can be refueled overnight from a mobile unit, ready to hit the road with cleaner fuel in the morning. This is especially handy for businesses operating out of leased properties or in areas without easy pipeline access.
The global demand for these flexible, cleaner fuel solutions is skyrocketing. The Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) virtual pipeline market alone was valued at around USD 1.6 billion recently. Experts expect that number to jump to USD 2.6 billion as more industries look for adaptable, low-emission energy. You can dig into these projections for the LNG virtual pipeline market at Future Market Insights.
Supporting Utilities with Peak Shaving
Even places with great pipeline infrastructure run into problems. During a brutal winter cold snap, for instance, the demand for natural gas can shoot through the roof as everyone cranks up the heat. This sudden surge can overtax the physical pipeline, causing pressure drops or, even worse, service outages.
This is where a strategy called "peak shaving" comes into play. A virtual pipeline can be brought in to inject extra gas into the system during these high-demand periods, keeping the grid stable and the heat on for customers.
LNG is the perfect tool for this job. A utility can keep LNG trucks on standby, ready to regasify the liquid and pump it directly into the local system the moment demand starts to peak. It’s a smart, targeted solution that prevents major disruptions without the colossal cost of building new, permanent pipelines that would just sit empty most of the year. It's all about ensuring reliability when it counts.
Common Questions About Virtual Pipelines
As the idea of a natural gas virtual pipeline starts to catch on, it’s only natural to have a few questions. This whole approach is a big shift from the underground pipes we’re all used to, so wondering about safety, practicality, and how it all works is completely normal.
To give you a clearer picture, we’ve put together answers to some of the most common questions we hear. Think of this as the practical side of virtual pipelines—the real-world details you need to know.
Is a Natural Gas Virtual Pipeline Safe?
Yes, absolutely. Safety isn't just a box to check; it’s the bedrock of the entire system. Every step, from how the equipment is designed to how it’s operated, is wrapped in layers of strict national and international standards.
The specialized containers used for both Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) and Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) are impressive pieces of engineering. They’re built to be incredibly durable, easily handling high pressures and extreme temperatures.
For instance, LNG tanks are basically giant, high-tech thermoses. They have a double-walled, vacuum-insulated design that keeps the LNG stable at its incredibly cold temperature. This tough construction means the cargo is secure, even on long hauls over rough roads.
On top of that, the entire logistics process is packed with modern safety tech.
- Real-Time IoT Monitoring: Each truck is fitted with sensors tracking pressure, temperature, and GPS location around the clock. If anything even hints at a problem, an alert goes out immediately.
- Highly Trained Personnel: The drivers and technicians handling the CNG and LNG aren't just truck drivers; they're specialists. They go through intensive training on safe handling and emergency response.
- Built-in Redundancies: The equipment itself, from valves to the systems used for offloading, has multiple safety features and backups designed to prevent any leaks or failures.
It’s this multi-layered approach that makes a natural gas virtual pipeline such a secure and reliable way to deliver energy.
When Is a Virtual Pipeline a Better Choice?
A virtual pipeline really shines where a physical pipeline is either impractical, way too expensive, or would simply take too long to build. It’s not about replacing traditional pipelines everywhere. It’s about having a smarter option for specific situations.
Think about the staggering upfront cost of building a traditional pipeline—it can run into millions of dollars per mile. For places with moderate energy needs or those in tricky terrain, that cost is often a non-starter.
A virtual pipeline becomes the clear winner in a few key scenarios:
- Tough-to-Reach Locations: For factories or communities tucked away in mountains or remote areas, digging a physical pipeline is often out of the question. A virtual pipeline can get anywhere a truck can.
- Fluctuating or Moderate Demand: It’s a perfect fit for a customer who doesn't use enough gas to justify their own pipeline, like a mid-sized manufacturing plant, a small industrial park, or a new housing development.
- Temporary Energy Needs: If you need power for a short-term construction project, a disaster relief effort, or even a large outdoor event, a virtual pipeline delivers it on-demand without permanent infrastructure.
- Peak Shaving for Utilities: During a cold snap, demand for gas spikes. Utilities use virtual pipelines to inject extra gas into the grid, avoiding the massive expense of building extra pipeline capacity that would sit idle 95% of the year.
The core advantage is flexibility. A virtual pipeline gets you out of the long-term commitment and massive financial hit of traditional infrastructure, delivering energy exactly when and where you need it.
This model lets you get energy flowing to a site in a matter of days or weeks, not the years it takes to plan, permit, and build a conventional pipeline.
What's the Difference Between a CNG and an LNG Virtual Pipeline?
While both deliver natural gas, the real difference comes down to the state of the gas—compressed versus liquid. That distinction changes its energy density and dictates which one is the right tool for the job.
With a CNG virtual pipeline, natural gas is squeezed under high pressure but stays a gas. This makes it a great, cost-effective solution for shorter distances and for customers with small to moderate energy needs, like a fleet of natural gas vehicles or a commercial building.
An LNG virtual pipeline, on the other hand, involves chilling the gas until it turns into a liquid. This process shrinks its volume by an incredible 600 times, packing way more energy into the same amount of space.
That density is a game-changer. A single truckload of LNG can deliver far more energy than a truckload of CNG. Because of this, LNG is the go-to choice for:
- Long-distance transport, where making fewer trips saves money.
- High-volume customers like big industrial plants, power generation stations, and large manufacturing facilities.
- Peak shaving operations, where a utility needs to push a massive amount of gas into the system fast.
The simple way to think about it is this: CNG is often the best economic choice for regional, lower-volume needs, while LNG’s incredible energy density makes it the champion for long-haul, high-demand applications.
For projects in North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, or Virginia facing natural gas connection delays or service interruptions, Blue Gas Express offers a fast and reliable solution. Our mobile CNG and LNG units can be deployed within hours to keep your operations running without a hitch. Don't let a utility delay stop your progress—visit Blue Gas Express to secure your temporary natural gas supply today.