Think of the vast network of natural gas pipelines crisscrossing the country as the arteries of our energy grid. If the pipelines are the arteries, then gas compressor stations are the powerful, strategically placed hearts that keep the whole system pumping. Without them, the natural gas that heats our homes, powers our factories, and generates our electricity would simply run out of steam.
The Unseen Engines of Our Energy Grid
As natural gas travels through a pipeline, it constantly loses momentum. Just like anything else in motion, it faces resistance—in this case, friction from rubbing against the pipe's inner walls. This friction causes the gas to lose pressure, a drag known as pressure drop. If you don't do anything about it, the gas will eventually slow to a crawl and stop long before it reaches its destination.
Counteracting the Inevitable Pressure Drop
To solve this problem, gas compressor stations are built along pipelines, usually every 40 to 70 miles. Each station acts like a booster shot. It pulls in the lower-pressure gas, uses powerful engines or turbines to re-compress it, and then pushes it back into the pipeline with renewed force. This cycle repeats all the way down the line, ensuring a steady, strong flow from the wellhead to the customer.
This simple but vital function supports a massive industry. The market for gas compressors is huge, reflecting just how critical they are for everything from new pipeline projects to liquefied natural gas (LNG) plants. To put it in perspective, one report valued the global gas compressors market at USD 5.1 billion and expects it to climb to around USD 6.9 billion by 2033. This growth shows just how much is being invested in keeping our energy infrastructure strong. You can explore more data on the global gas compressors market from industry analysts.
Key Functions of a Gas Compressor Station
So, what are the core jobs of these stations? It really boils down to a few essential tasks that keep the entire natural gas transportation system running smoothly.
| Function | Core Purpose |
|---|---|
| Pressure Boosting | To increase gas pressure, overcoming friction and elevation changes in the pipeline. |
| Maintaining Flow | To ensure a consistent and reliable volume of natural gas reaches its destination. |
| Enabling Long-Distance Transport | To make it possible to move gas hundreds or even thousands of miles from production fields. |
At the end of the day, gas compressor stations are the unsung heroes of our energy infrastructure. They operate quietly in the background, doing one thing exceptionally well: keeping the pressure up and the gas moving. It’s because of them that when you turn on your stove or crank up the heat, the energy you need is always there, right on cue.
A Look Inside a Gas Compressor Station
To get a real feel for how a gas compressor station works, you have to look under the hood. While no two facilities are exactly alike, they all rely on the same fundamental components working together to pull in natural gas, pressurize it, and send it back on its way down the pipeline. It’s a lot like a highly specialized factory, where each machine has one critical job to do.
This concept map gives you a great visual of the station's role. It's the heart of the pipeline, taking in gas, giving it the pressure boost it needs, and making sure it gets where it's going.
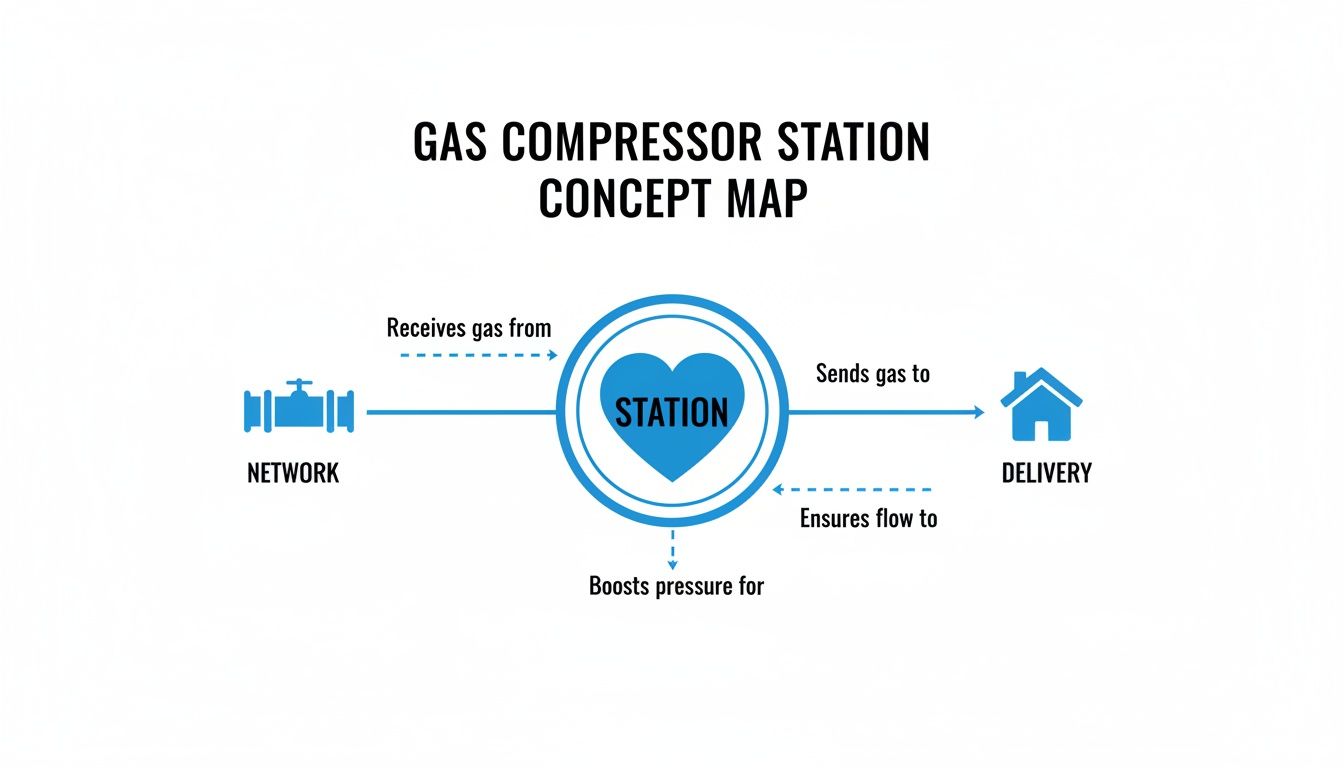
The station is the crucial link that overcomes the natural pressure drop that happens as gas travels over long distances. The whole operation depends on just a few key pieces of equipment running in a very specific order.
The Power Source: The Prime Mover
Every compressor station needs a serious engine to run the show. We call this the prime mover, and it’s what provides the raw power needed to compress all that natural gas. In the field, you'll typically run into two main types:
- Natural Gas Turbines: Think of a jet engine, but instead of pushing a plane forward, it’s bolted to the ground and modified to spin a massive shaft. These things are workhorses. They're incredibly powerful and usually run on a tiny siphon of the same pipeline gas they're pushing, which makes them pretty self-sufficient.
- Electric Motors: Where reliable and affordable electricity is available, massive industrial electric motors are a fantastic option. They’re generally quieter and have zero emissions on-site, which can be a huge plus when it comes to getting permits and meeting environmental standards.
The decision to go with a turbine versus an electric motor really comes down to the specifics of the site—local utility costs, air quality regulations, and just how much horsepower is needed.
The Heart of the Operation: The Compressor Unit
The prime mover delivers the muscle, but the compressor unit is where the real work happens. It’s hooked directly to the prime mover’s shaft and is the machine that physically squeezes the gas, forcing the molecules closer together to jack up the pressure.
At its core, the compressor is simply a powerful pump designed specifically for gas. It takes in low-pressure gas from the incoming pipeline and pushes out high-pressure gas into the outgoing line, providing the energy needed to continue the journey.
We’ll dig into the different compressor designs, like reciprocating and centrifugal, a bit later. For now, just know this is the component doing all the heavy lifting.
Keeping Things Clean and Cool: Support Systems
Before and after compression, the gas needs some conditioning to protect the pipeline and keep everything running smoothly. Compressing gas creates an incredible amount of heat, and if you don't manage it, you can cause serious damage to the equipment. That's where the support systems come in.
Several systems work in tandem to get the gas ready:
- Scrubbers and Filters: As gas flows into the station, its first stop is the scrubbers. These are basically giant filters that use separators and other tech to strip out any liquids, dirt, or other junk that could wreck the delicate, high-speed parts inside the compressor.
- Cooling Systems: Once the gas is compressed, it's screaming hot. It has to be cooled down before it can safely go back into the main pipeline. You’ll see huge aerial coolers—they look like giant car radiators with massive fans—that pull that heat out and bring the gas temperature back to a safe level.
- Yard Piping and Valves: A whole web of pipes and automated valves, called "yard piping," controls how the gas moves through the facility. This network lets operators bypass the entire station for maintenance or quickly shut down specific sections if there's an emergency.
Put it all together, and you have a sophisticated system with a single purpose: keeping natural gas flowing safely and reliably across the country.
Comparing Compressor Types for Different Applications
Not all compressors are created equal, and picking the right one is a make-or-break decision when designing a gas compressor station. This choice has a huge ripple effect on the station's efficiency, budget, and how it operates day-to-day. The industry really boils down to two main designs, each with a completely different way of getting the job done.
Understanding these two workhorses—reciprocating and centrifugal compressors—is key. A good way to think about it is that a reciprocating compressor is like a powerful, methodical bicycle pump, while a centrifugal compressor is more like a high-speed fan, using pure rotational force. Their mechanical differences make them suited for very different jobs across the natural gas supply chain.
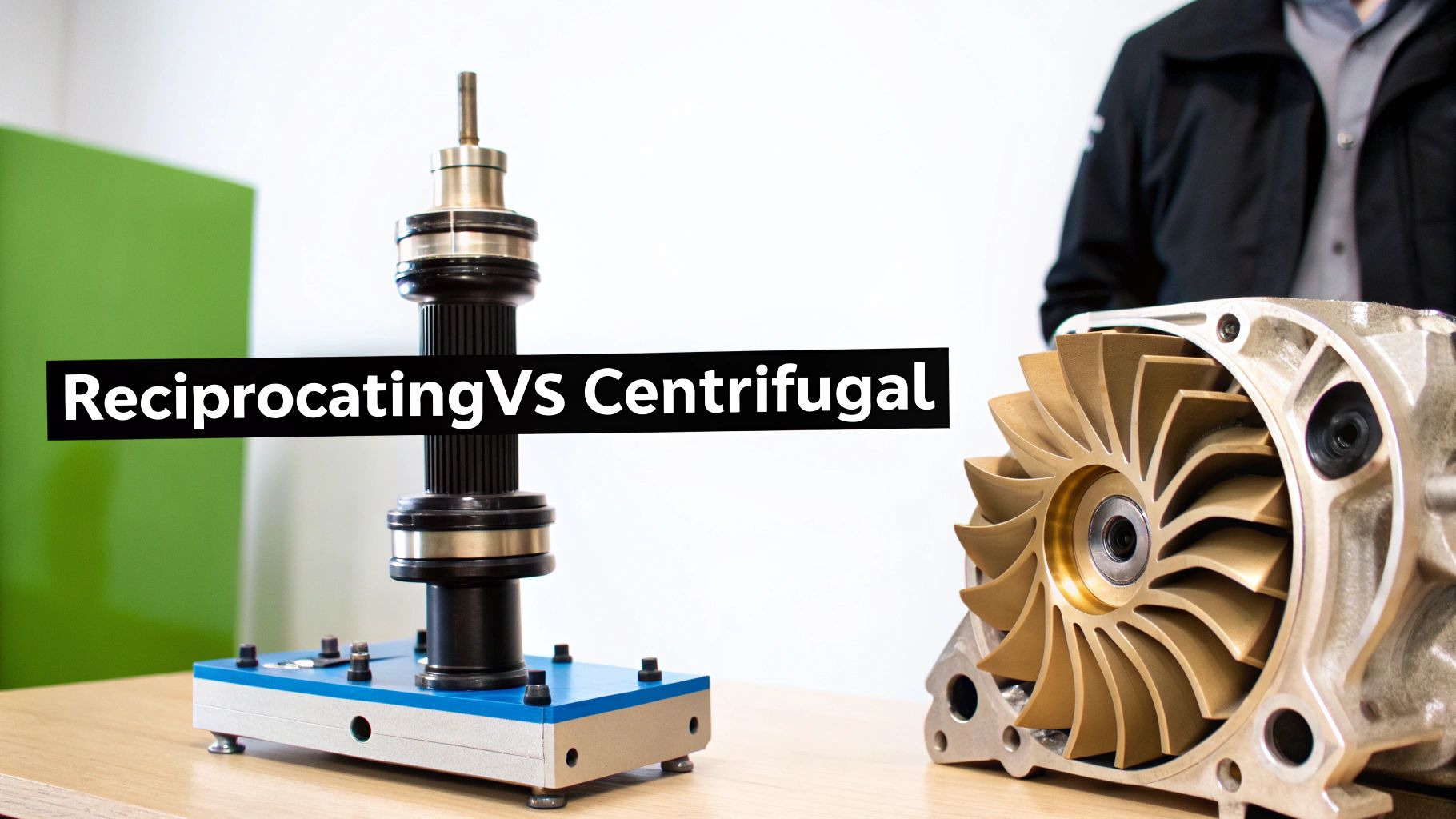
The Power of Positive Displacement: Reciprocating Compressors
A reciprocating compressor works by using a piston that moves back and forth inside a cylinder to physically squeeze the gas. On the downstroke, it pulls gas in. On the upstroke, it traps that set volume of gas and compresses it, forcing it out at a much higher pressure.
This positive displacement method is incredibly effective for jobs that need very high pressures but are dealing with lower or fluctuating gas flow rates.
- Best Use Cases: These are the go-to choice for gas gathering systems where suction pressures can be all over the place, gas storage facilities that inject gas deep underground, and certain specialized processing applications.
- Operational Traits: They're highly efficient across a wide range of operating conditions but come with a higher maintenance burden due to their many moving parts like pistons, rings, and valves.
The Force of Dynamic Motion: Centrifugal Compressors
On the other hand, a centrifugal compressor uses a rapidly spinning impeller—a wheel with angled blades—to pressurize gas. Gas is drawn into the center of the impeller and then flung outward at incredible speed. This velocity is converted into pressure as the gas slows down in a surrounding diffuser.
This dynamic compression approach is perfect for moving massive volumes of gas in a continuous, smooth flow.
Because they are built for high-volume, steady-state operations, centrifugal compressors are the undisputed champions of long-haul natural gas transmission pipelines. Their ability to handle immense flow rates makes them essential for interstate and cross-country gas transport.
You can see their importance reflected in global infrastructure. As countries expand their energy networks, the demand for these powerful compressors skyrockets. China’s transmission network, for example, has swelled to over 120,000 kilometers of pipeline—a massive system that depends on hundreds of high-pressure compressor stations to keep the gas moving. You can find more insights on the connection between infrastructure growth and the global natural gas compressor market.
A Head-to-Head Comparison
Choosing between these two types of compressors always involves a series of trade-offs. Engineers have to carefully weigh factors like flow rate, required pressure ratio, operational flexibility, and long-term maintenance costs. To make it easier to see the differences at a glance, here’s a quick breakdown.
Reciprocating vs Centrifugal Compressors
| Feature | Reciprocating Compressor | Centrifugal Compressor |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Principle | Positive displacement (piston-driven) | Dynamic (impeller-driven) |
| Best For | High pressure, low to medium flow | High flow, moderate pressure |
| Flow Rate | Handles variable and low flow rates well | Requires steady, high-volume flow |
| Pressure Ratio | Achieves very high compression ratios per stage | Lower compression ratios per stage |
| Efficiency | Highly efficient across a broad operational range | Most efficient at a specific design point |
| Maintenance | Higher maintenance due to more wearing parts | Lower maintenance with fewer moving parts |
| Common Use | Gas gathering, storage, and processing | Mainline transmission pipelines |
Ultimately, the decision directly shapes the performance and economics of the gas compressor station. Getting it right from the start is crucial for a successful project.
How Safety and Maintenance Keep the Gas Flowing
When you're dealing with natural gas transmission, there's absolutely no room for error. A single hiccup at a gas compressor station can create a domino effect, interrupting energy delivery for thousands and creating serious safety risks. That's why ironclad safety protocols and a forward-thinking maintenance plan are the bedrock of any reliable station.
These aren't just buildings full of machinery; they're meticulously engineered environments where safety dictates every decision. Everything from automated shutdown systems to 24/7 remote monitoring is there for one reason: to catch a potential problem before it becomes a real one.
Skimping on safety and maintenance isn't just cutting corners—it’s inviting disaster. It's a surefire way to end up with costly downtime, operational failures, and potential environmental headaches. A well-maintained station is a safe and efficient one. Simple as that.
Engineered Safety Systems on Site
Modern compressor stations are packed with smart safety systems that act like a digital nervous system, constantly monitoring operations and ready to react instantly. Think of them as a vigilant guardian that never sleeps, protecting the crew, the equipment, and the surrounding area.
Here are a few key players in that system:
- Emergency Shutdown (ESD) Systems: These are the big red buttons, but automated. If they detect dangerously high pressure, a gas leak, or a fire, they can shut down the entire station or just a single piece of equipment in the blink of an eye.
- Gas Detection and Fire Suppression: Throughout the facility, hyper-sensitive sensors are always sniffing the air. If they pick up even the tiniest trace of natural gas, alarms blare, ventilation fans kick into high gear, and fire suppression systems are put on standby.
- Pressure Relief Valves: These are the simple, yet brilliant, mechanical fail-safes. If pressure inside a pipe or tank builds up beyond a safe limit, these valves automatically open to vent the excess gas, preventing a catastrophic rupture.
These built-in controls are the first line of defense, but they’re only as good as the human oversight and maintenance that back them up.
The Critical Role of Preventative Maintenance
While emergency systems are there to react to a problem, preventative maintenance is all about making sure those problems never happen in the first place. It's the difference between calling the fire department when your house is burning and having an inspector regularly check your wiring to prevent a fire.
A proactive maintenance schedule is the single most important factor in ensuring the long-term reliability and safety of a gas compressor station. It transitions operations from a reactive "fix-it-when-it-breaks" model to a predictive and preventative strategy that minimizes unplanned outages.
This means following a detailed calendar of tasks, from quick daily checks to major annual overhauls. To keep these critical tasks on track, it's vital to have clear, repeatable processes. Discovering a better way to document procedures can make all the difference in ensuring safety and maintenance are done right every single time.
A Look at a Typical Maintenance Schedule
A solid maintenance program is incredibly detailed, covering every nut, bolt, and sensor. Nothing gets overlooked.
A typical routine might look something like this:
- Daily Walk-Arounds: Operators start their shifts by walking the site, using their eyes and ears to spot anything out of the ordinary—unusual noises, vibrations, or odd readings on pressure and temperature gauges.
- Routine Lubrication and Fluid Analysis: Just like your car, compressors and their engines need regular oil changes and fluid top-offs. Technicians also take oil samples for lab analysis, which can reveal early signs of internal wear long before a part fails.
- Vibration Analysis: Using specialized sensors, technicians can measure the vibration of a running compressor. A subtle change in the vibration pattern can be an early warning sign of a failing bearing or a misaligned shaft.
- Component Testing and Calibration: All those safety sensors, valves, and shutdown systems are tested on a regular basis to make sure they'll work perfectly when they're needed most.
At the end of the day, this relentless focus on safety and maintenance is what allows gas compressor stations to run like clockwork, keeping the lights on and homes warm without interruption.
Using Mobile Gas Solutions to Bridge Infrastructure Gaps
Permanent gas compressor stations are the heavy-duty workhorses of our natural gas grid, but they aren't invincible. When construction, major upgrades, or planned maintenance take a station offline for weeks or even months, it creates a serious gap in the energy supply chain. Likewise, new construction projects often need natural gas access long before the permanent utility pipeline is completed and commissioned.
In these situations, just waiting isn't really an option. Project timelines get derailed, businesses can lose revenue, and in cold weather, safety becomes a real concern. This is exactly where mobile natural gas solutions come into play, acting as a flexible, rapidly deployed "virtual pipeline" that bridges the gap until permanent infrastructure is back online.

These temporary systems—which deliver either compressed natural gas (CNG) or liquefied natural gas (LNG) by truck—provide an on-demand energy supply precisely when and where it's needed most. Think of them not just as a backup plan, but as a strategic tool for ensuring things keep running smoothly.
Keeping Construction Projects on Schedule
Picture this: a brand-new commercial building is finished and ready for tenants, but the final gas line connection is delayed by several weeks. Without natural gas to run the HVAC systems, the building can't pass inspection or get its certificate of occupancy. Every single day of delay means lost lease revenue and mounting costs for the developer.
This is a classic scenario where a mobile gas service saves the day. A temporary CNG or LNG unit can be brought right to the site, connected to the building's internal gas system, and provide the fuel needed to commission all the equipment and secure that crucial occupancy permit.
This same principle applies to countless other construction scenarios:
- Residential Developments: You can make sure new homes have heat and hot water right on schedule, even if the main gas line for the whole subdivision isn't active yet.
- Industrial Facilities: It allows for the commissioning of large gas-fired generators or specialized process equipment without having to wait on the utility's schedule.
- Temporary Heating: Mobile gas can fuel large construction heaters, allowing interior work like drywall and painting to continue right through the cold winter months.
By decoupling the project timeline from the utility's schedule, mobile gas gives builders and developers the power to maintain momentum and stay in control of their deadlines.
Ensuring Uptime During Maintenance and Outages
Even the most reliable gas compressor stations and pipelines need periodic maintenance. During these planned shutdowns, a segment of the gas network is isolated, which could cut off service to downstream customers. Unexpected disruptions happen, too—winter storms can freeze equipment like wellheads and pipelines, as we saw during the 2021 Texas Freeze.
In these instances, mobile natural gas serves as an essential form of energy insurance. By injecting gas from a temporary supply directly into the pipeline downstream of the outage, utilities can create a seamless bypass that keeps their customers online without a single interruption.
This proactive approach prevents costly disruptions for commercial and industrial clients who depend on a steady gas supply for their daily operations. It’s a critical service that helps maintain public trust and ensures energy reliability when the permanent grid is temporarily down.
The Growing Need for Mobile Energy Flexibility
The demand for these flexible solutions is on the rise. Compressed natural gas (CNG) compressors are a rapidly expanding market, driven by everything from vehicle fleet conversions to new urban gas distribution projects. This growth highlights a clear need for mobile CNG services to fill supply gaps along the way. Market forecasts project the CNG compressor segment will grow from about USD 4.38 billion to approximately USD 6.04 billion by 2032.
Operationally, temporary mobile CNG units are perfectly positioned to meet short-term, high-pressure gas needs, whether it's for construction permits, equipment commissioning, or freeze protection during pipeline tie-ins. If you're interested in the market forces behind this, you can find additional details on CNG compressor market growth.
Ultimately, mobile gas solutions are a vital complement to the permanent infrastructure of gas compressor stations. They provide the agility and speed needed to navigate the logistical headaches of construction, maintenance, and emergencies, making sure the energy keeps flowing no matter what.
Keeping Your Projects and the Gas Moving
Throughout this guide, we've pulled back the curtain on gas compressor stations. They're the real workhorses of our energy system, constantly pushing gas through the vast network of pipelines that power our homes and businesses. We’ve looked under the hood at their core components, weighed the pros and cons of different compressor types, and driven home why safety and solid maintenance are absolutely critical.
But here’s the thing about permanent infrastructure: it’s powerful, but it isn't flexible. For anyone managing a construction project or a utility, this rigidity can be a huge problem. Every planned upgrade, every unexpected outage, and every new pipeline connection creates a potential gap in the gas supply. And a gap in supply means everything grinds to a halt.
A Virtual Pipeline When You Need It Most
So, what happens when you’re building a new facility and need to commission equipment before the main gas line is live? Or when a critical station has to shut down for a week of essential maintenance?
This is precisely where mobile gas solutions from providers like Blue Gas Express come in. By trucking in compressed natural gas (CNG), they essentially create an on-demand, temporary pipeline right where you need it, for exactly as long as you need it.
What could have been a project-stopping crisis becomes just another box to check on the logistics plan.
Think of mobile gas as an energy lifeline. It's a "virtual pipeline" that steps in to keep the supply flowing seamlessly when the physical pipes are out of commission, ensuring costly delays and disruptions are a thing of the past.
This approach is a game-changer. It means construction timelines stay on track. It allows factories to fire up and test new equipment without waiting on the utility. Most importantly, it lets gas companies perform vital maintenance and upgrades without ever having to tell their customers the gas is off.
In the end, it’s all about having a nimble, ready-to-go solution in your back pocket. That ability to adapt is what separates a smooth, successful project from a logistical nightmare.
Common Questions About Gas Compressor Stations
When you're dealing with energy infrastructure, a lot of questions come up, especially when project deadlines and keeping the gas flowing are on the line. For project managers and facility operators, getting a handle on the real-world details of gas compressor stations is key. Here are some straightforward answers to the questions we hear most often.
How Long Does It Take to Build a Permanent Compressor Station?
Putting up a permanent gas compressor station is a major undertaking, not something that happens overnight. The timeline is long and involved, starting with detailed planning and navigating a maze of regulatory permits before you even get to engineering design and the actual construction.
From the first blueprint to turning the key, you're easily looking at a timeline of 18 months to several years. The exact duration really boils down to the station's size, where it's located, and the layers of local, state, and federal rules you have to follow. This long development cycle is a huge reason why so many projects rely on temporary mobile gas solutions to fill the gap and avoid expensive delays in firing up equipment or getting an occupancy permit.
What Happens When a Compressor Station Goes Offline?
When a compressor station shuts down, whether for planned maintenance or an unexpected repair, the natural gas flow through that part of the pipeline grinds to a halt. For every business, factory, and neighborhood downstream, that can mean a complete service blackout.
To keep that from happening, gas utilities have a smart playbook that often involves bringing in temporary mobile solutions.
- Creating a Virtual Pipeline: Mobile units are brought to the site to inject compressed natural gas (CNG) directly into the pipeline, but past the point of the outage.
- Ensuring an Uninterrupted Supply: This essentially creates a "virtual pipeline" that bypasses the offline station, so customers keep their gas supply without noticing a thing.
- Maintaining Operational Continuity: It's a critical strategy for preventing costly shutdowns and keeping the energy supply stable for everyone who depends on it.
This proactive approach is absolutely essential for maintaining customer trust and ensuring a reliable energy grid while necessary infrastructure work gets done.
Can a Temporary Gas Solution Really Power a Large Project?
Yes, absolutely. It's a common myth that temporary solutions are only for small-scale, emergency needs. The truth is, modern mobile natural gas systems are designed to be highly scalable and are engineered to handle a huge range of demanding projects.
Specialized equipment is used to bring CNG or LNG to a site, where it's then regulated to the exact pressure and flow rate the customer's system needs. The whole setup is designed to integrate seamlessly.
Whether you're heating a massive new commercial building, commissioning a whole bank of industrial power generators, or fueling a high-volume manufacturing line, these temporary systems are built to deliver a reliable, utility-grade natural gas supply whenever and wherever you need it.
Are Compressor Stations Noisy or Bad for the Environment?
Permanent gas compressor stations are industrial facilities, so they do make noise, mostly from the big prime movers like gas turbines. That said, modern stations are built with serious noise-reduction technology, including specialized buildings and insulation, to make sure they stay within strict local and federal noise limits.
Environmentally, the biggest concern is methane emissions. Since methane is a potent greenhouse gas, minimizing leaks is a huge priority for the industry. Stations are outfitted with advanced monitoring systems to find and fix leaks fast. It's also worth noting that a large share of methane emissions in the oil and gas sector comes from many smaller, scattered sources, not just big facilities like compressor stations. In fact, recent research shows that sites emitting less than 100 kilograms of methane per hour are responsible for 70% of all emissions from U.S. onshore oil and gas operations.
When permanent infrastructure is delayed or offline, your project doesn't have to stop. Blue Gas Express provides the essential bridge with reliable, on-demand mobile natural gas solutions, ensuring your operations continue without interruption. Keep your project moving forward by visiting https://bluegasexpress.com to learn how we can support your energy needs.