What if you could fill up your car's tank every night while you sleep, right in your own garage? That's the core idea behind a CNG home fueling station. It works a lot like plugging in an electric car, but instead of electricity, you're using the same natural gas that already runs your furnace and water heater.
How a Home CNG Fueling Station Works
Think of a home CNG station as a powerful appliance that takes the low-pressure natural gas from your utility line and transforms it into high-pressure fuel ready for your vehicle. It essentially creates a direct link between your home's gas supply and your car, cutting out the need to ever visit a public fueling station again.
The process starts with your residential natural gas line. The gas flowing into your house is at a very low pressure—usually less than 1 psi (pounds per square inch)—which is perfect for a stove but nowhere near enough to give a vehicle any meaningful driving range. This is where the real work begins.
The Compression Cycle
The heart of the system is the compressor. This machine pulls in that low-pressure gas and, just as the name implies, compresses it. The target is to crank the pressure all the way up to around 3,600 psi. This intense pressure is what allows you to pack enough gas into your vehicle's tank for a decent trip.
But before the gas gets fully squeezed, it has to be cleaned up. It passes through a dryer that strips out any moisture and other impurities. Getting rid of that water vapor is a critical step; it prevents corrosion from forming inside your vehicle's fuel system and ensures the gas burns as cleanly and efficiently as possible.
This diagram lays out the simple, direct journey from your gas meter to your car.
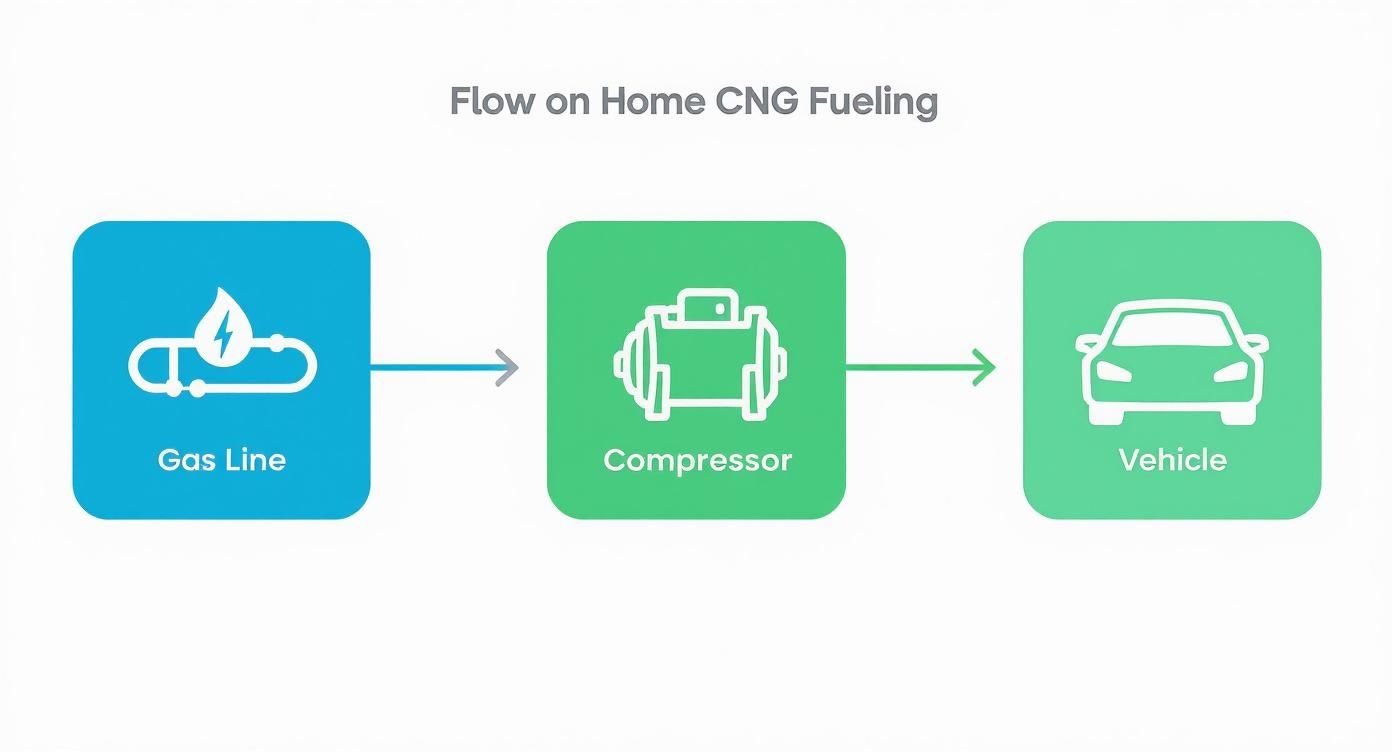
As you can see, it's a straightforward, three-step flow: tap the gas line, compress the gas, and then fill the vehicle.
Once the gas is compressed and dried, it’s ready to go. A heavy-duty, high-pressure hose connects the fueling unit directly to your CNG vehicle's filling port. You just hook it up, and the appliance does the rest, automatically shutting off when the tank is full.
To help you visualize the main parts involved, here's a quick breakdown of what makes up a typical home fueling setup.
Key Components of a Home CNG Fueling System
| Component | Function | Analogy |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Inlet | Taps into your home's low-pressure natural gas line. | It's like the water intake hose on a pressure washer. |
| Dryer/Filter | Removes moisture and impurities from the gas. | A water filter for your natural gas. |
| Compressor | Increases gas pressure from <1 psi to ~3,600 psi. | A super-powered bicycle pump for your car. |
| Dispensing Hose | A reinforced, high-pressure hose to fill the vehicle. | The fueling nozzle you'd find at a gas station pump. |
Each of these parts has a specific job, working together to make at-home fueling safe and effective. It's a surprisingly simple concept for such a powerful piece of technology.
A home CNG fueling station represents a personal piece of a much larger energy puzzle. These systems allow individuals to tap into a cleaner, domestically sourced fuel right from their garage or driveway.
This isn't just a niche hobby, either. The global market for natural gas fueling stations was valued at around USD 47.74 billion in 2025 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of nearly 6.6% through 2033. This trend is part of a bigger move toward more sustainable transportation.
Modern home compressors that can safely operate between 200–250 bar (that’s roughly 2,900–3,600 psi) are making this a more realistic option than ever. You can dig deeper into the market trends for natural gas filling stations to see where the industry is heading.
Choosing Between Slow-Fill and Fast-Fill Systems
When you're looking into a CNG home fueling station, your first big decision is whether to go with a slow-fill or a fast-fill system. This choice really shapes your daily routine, how much you'll spend upfront, and how complicated the installation will be. Think of it like charging an electric car: you can use a slow trickle charger overnight or a high-powered supercharger at a public station. Both fill up the "tank," but they work on completely different timelines.
Your driving habits are the best guide here. For most homeowners, a slow-fill system makes the most sense. It’s built for overnight convenience. A fast-fill system, on the other hand, delivers gas-station speed but comes with a much bigger price tag and complexity, which is why you almost never see them at a private residence.

The Slow-Fill Approach: Set It and Forget It
A slow-fill system hooks right into your home's natural gas line and uses a small, steady compressor to fill your vehicle’s tank over several hours. It’s incredibly simple. You come home, connect the hose to your car, and let it run overnight. When you wake up, your tank is full, and you're ready to go.
This approach is perfect for the average daily driver who doesn’t need a five-minute fill-up. It's the most budget-friendly and straightforward type of cng home fueling station to install, taking up less space and needing a less beefy electrical connection than a fast-fill setup.
- Best For: Commuters, local drivers, and anyone who can let their vehicle refuel while they sleep.
- Typical Fill Time: 6-10 hours for an average passenger car.
- Key Advantage: Significantly lower equipment and installation costs.
The real beauty of a slow-fill system is how seamlessly it fits into your life. It doesn't need a separate, high-pressure storage tank because the compressor sends gas directly from your utility line into your vehicle. This direct-to-vehicle method is what keeps the system’s footprint and cost manageable for a typical home garage.
The Fast-Fill System: Power and Speed
A fast-fill system works a lot more like the pump at a commercial CNG station. Instead of pushing gas directly into your car, its powerful compressor first fills a series of large, high-pressure storage tanks, often called a "cascade storage system." These tanks essentially act as a reservoir, holding a large volume of compressed gas at the ready.
When it's time to refuel, the system transfers that stored gas from the tanks into your vehicle at high speed. This lets you fill up in just a few minutes—about the same time it takes to pump gasoline.
Fast-fill systems prioritize speed by pre-compressing and storing gas. This allows for a quick transfer to the vehicle but requires a more complex, expensive, and space-intensive setup that is generally better suited for commercial fleets rather than individual homeowners.
Of course, that kind of performance comes with some serious trade-offs. Fast-fill systems demand a much larger, more powerful compressor, dedicated space for the bulky storage tanks, and a heavy-duty electrical supply. All these factors drive the cost way up, making them a very rare choice for a single-family home.
Comparison: Slow-Fill vs. Fast-Fill Home CNG Systems
To make the decision clearer, it helps to see the two systems side-by-side. Each has a distinct purpose, and what works for a commercial fleet is usually overkill for a daily commuter.
Slow-Fill vs. Fast-Fill Home CNG Systems
| Feature | Slow-Fill System | Fast-Fill System |
|---|---|---|
| Refueling Time | 6-10 hours (overnight) | 5-10 minutes |
| Upfront Cost | Lower | Significantly Higher |
| Core Equipment | Small compressor | Large compressor, high-pressure storage tanks |
| Space Required | Minimal (small wall-mounted unit) | Substantial (for compressor and tanks) |
| Installation | Simpler, connects to existing gas/electric | Complex, requires robust infrastructure |
| Best Use Case | Individual homeowners, daily commuters | Commercial fleets, high-usage vehicles |
For nearly everyone considering a home unit, the table makes the choice obvious. The convenience and cost-effectiveness of a slow-fill system are hard to beat for residential use.
Making the Right Choice for Your Home
The technology behind these home units is really just a scaled-down version of what's used at public stations. The U.S. has a long history with CNG infrastructure, with around 1,200 public and private stations already in operation. Home fueling systems simply adapt that proven technology, using smart compressors that automatically manage gas flow for safety and efficiency. This is tech that has been refined for decades. If you're interested in the bigger picture, you can learn more about the broader CNG infrastructure and its benefits.
When it comes down to it, the slow-fill system is the practical, logical choice for almost every residential user. It delivers on the biggest promise of home fueling: the simple luxury of waking up to a full tank every morning, without ever having to stop at a gas station again.
Calculating the Cost and Your Return on Investment
For most people, the decision to install a CNG home fueling station comes down to a single, make-or-break question: does it actually make financial sense? The convenience is a huge plus, but let's be honest, the numbers have to work. This means looking past the initial price tag and figuring out how—and when—the long-term fuel savings will pay you back.
The money you'll spend upfront really falls into two buckets: the fueling appliance itself and the professional installation.
Breaking Down the Upfront Costs
The heart of the system, the fueling appliance, is your biggest initial expense. You can expect these units to run anywhere from $4,500 to over $10,000. The price difference comes down to brand, capacity, and features. A basic slow-fill unit will sit at the lower end of that range, while a more powerful model with a faster compression rate or smarter diagnostics will push the cost higher.
Next, you have installation, and this is absolutely not a weekend DIY project. You’ll need certified pros for this part, which typically adds another $2,000 to $6,000 to your total. This cost covers a licensed plumber to safely tap into your home's natural gas line and an electrician to wire the unit, which almost always requires its own dedicated circuit. Be aware that if your home's gas or electrical systems need an upgrade to handle the new load, that could drive the installation price up.
All in, you should plan on a total upfront investment between $6,500 and $16,000. It’s a significant number, for sure, but think of it as the starting line for a race toward long-term savings.
Analyzing Your Long-Term Savings
This is where installing your own CNG station starts to get exciting. Your return on investment, or ROI, comes directly from the price gap between the cheap natural gas flowing into your home and the gasoline or diesel you buy at the pump. To make a fair comparison, we convert the cost of natural gas into a gasoline gallon equivalent (GGE).
While gas prices are on a perpetual rollercoaster, your residential natural gas rates are usually much more stable and almost always far lower. For instance, if gasoline in your area is selling for $3.50 per gallon, the equivalent amount of natural gas might only cost you $1.00 to $1.50. That’s an instant savings of $2.00 or more every single time you fill up your tank.
This growing appeal isn't just a niche trend. The global market for compressed natural gas was valued at around USD 12.46 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit USD 22.48 billion by 2032. That kind of growth is a clear signal that the cost and convenience benefits are catching on with more drivers and fleet managers. You can dig into the numbers and see the projected growth of the CNG market for yourself.
A Sample ROI Calculation
Okay, let's run the numbers on a real-world scenario to see how this plays out.
Imagine a daily commuter who drives a CNG-converted pickup truck.
- Total Upfront Cost: We'll use a mid-range figure of $10,000 for the unit and professional installation.
- Daily Commute: 50 miles, round trip.
- Vehicle Efficiency: The truck averages 15 miles per GGE.
- Daily Fuel Needed: 50 miles ÷ 15 miles/GGE = 3.33 GGE.
- Fuel Cost Savings: Local gasoline is $3.75/gallon, while their natural gas cost works out to $1.25/GGE. That’s a savings of $2.50 per GGE.
Now, let's see how quickly that adds up:
- Daily Savings: 3.33 GGE x $2.50/GGE = $8.33 saved every workday.
- Annual Savings: $8.33/day x 250 workdays/year = $2,082 saved per year.
- Payback Period: $10,000 (initial cost) ÷ $2,082 (annual savings) = Roughly 4.8 years.
In this case, the entire system pays for itself in just under five years. From that point forward, the $2,000+ saved each year is pure cash back in their pocket, cutting down their vehicle operating costs for as long as they own it. And remember, the more you drive, the faster you hit that break-even point.
Sorting Out Installation and Permits
Putting a CNG fueling station at your home isn't like plugging in a new washing machine. Think of it more as a serious infrastructure project—one that demands a professional touch from start to finish. This is not a weekend warrior DIY job; it's a carefully coordinated process that needs certified technicians to ensure everything is safe, compliant, and works as it should.
In many ways, the process is a lot like planning a house extension, including costs and permits. You need proper plans, official approvals, and skilled tradespeople. You wouldn't dream of building a new room onto your house without permits and a good builder, and the same logic applies here.
What Your Property Needs for a Smooth Installation
Before any work can even begin, your property has to check a few critical boxes. These aren't just suggestions; they're absolute must-haves for the safety and performance of your CNG home fueling station. Any good installer will do a full site check, but it helps to know what they'll be looking for.
A successful installation really boils down to three things:
- The Right Spot and a Solid Base: The compressor unit needs a dedicated home. Even if it's wall-mounted, it has to be on a stable surface that can handle its weight and the subtle vibrations it creates while running. The area needs to be clear of clutter.
- Plenty of Airflow: Natural gas is lighter than air, so it tends to rise and disperse. Still, good ventilation is a non-negotiable safety feature. If you’re installing in a garage, you need to have enough airflow to ensure gas can't build up, a detail your installer will confirm based on local codes.
- Utility Hookups: The compressor needs two things to run. A licensed plumber has to tap into your home's natural gas line, and a certified electrician must install a dedicated electrical circuit. These compressors pull a lot of juice, so they can't just be plugged into any old outlet.
Making Sense of the Permitting Process
Getting the right permits is often the trickiest part of the whole project. It's not a one-and-done deal; you'll need green lights from several different authorities, and each one plays by its own rulebook. This is a huge reason why you want an experienced installation company in your corner—they know how to navigate the bureaucracy.
Your installer should handle most of the paperwork, but you’ll want to know who has a say. The main players are your local building authority (the city or county) and your natural gas utility provider.
Getting the right permits isn’t just about following the rules—it's a critical safety check. Every approval you get is another confirmation that your setup meets the standards designed to keep your home, family, and neighborhood safe.
The journey usually starts with submitting detailed installation plans, including diagrams for all the gas and electrical work. Officials review these documents to make sure they meet code. Once they give their approval, the real work can begin. After everything is installed, a final inspection is mandatory to confirm the work matches the approved plans before you can legally start fueling up.
Finding the Right Installer
Your choice of installer can make or break this project. A great company doesn't just know the technical side; they act as your guide through the entire regulatory maze. You want someone with a solid track record of installing these exact systems right in your area.
When you're talking to potential installers, have a few key questions ready:
- Licenses and Certifications: Are your plumbers and electricians fully licensed? More importantly, are they certified to work on natural gas systems and high-power electrical circuits?
- Permitting Track Record: Can you show me examples of other projects you've successfully permitted with my local building department and gas company?
- Project Timeline: From the first site visit to the final inspection, how long do you expect this to take?
- Itemized Quote: Can I get a detailed quote that breaks down the costs? I want to see separate line items for the equipment, labor, permit fees, and anything else.
Asking these questions upfront helps you make a smart decision and ensures your fueling station gets installed safely, legally, and without any nasty surprises.
Understanding Safety and Routine Maintenance
Let's be clear: bringing a high-pressure fueling system into your home demands a serious commitment to safety. While a modern cng home fueling station is designed with layers of protection, you are the most important part of the safety equation. Think of it this way: the system is built for reliability, but your routine upkeep is what guarantees it operates securely for years to come.
Modern fueling units are packed with built-in safety mechanisms—these aren't optional extras, they're core to the design.
- Automatic Shut-Offs: The compressor is always monitoring pressure. When your vehicle's tank hits its 3,600 psi limit, the system instantly cuts the gas flow. No chance of over-pressurization.
- Pressure Relief Valves: In the rare case that pressure somehow builds beyond a safe level, these valves automatically vent gas to bring everything back to normal.
- Methane Detectors: Many systems have integrated sensors that sniff the air for even tiny amounts of natural gas. If a leak is detected, the unit shuts down and sounds an alarm.

Your Role in Home Fueling Safety
Beyond the automated tech, your own awareness is crucial. Gas utilities add an odorant called mercaptan to natural gas, which gives it that distinct "rotten egg" smell. This is your first and best alert system.
If you ever smell gas, act immediately. Don't touch any light switches or electrical devices. Leave the area, and from a safe distance, call your gas utility's emergency line. Since CNG is flammable, knowing how to operate a fire extinguisher effectively is a non-negotiable skill. It's also just good practice to keep the area around the unit clean and clear to ensure good ventilation and prevent accidents.
Safety isn't just about the equipment; it's a routine. Simple habits like inspecting the hose before each use and keeping the area clear are fundamental to the secure operation of your home fueling system.
A Simple Maintenance Schedule
The good news is that routine maintenance is pretty simple. It's a lot like changing the oil in your car—a small task that prevents huge problems. Your installer will give you a specific checklist, but most maintenance plans look something like this.
Monthly Homeowner Checks:
- Visual Inspection: Give the dispensing hose a quick once-over. Look for any cracks, frays, or signs of wear.
- Area Check: Make sure the space around the unit is clean, dry, and free of clutter.
- Listen: When the compressor is running, does it sound normal? Or are there any new, unusual noises?
Annual Professional Service:
- Filter Changes: The system has filters that need to be replaced annually by a certified technician to keep impurities out of the gas.
- System Calibration: The technician will double-check all the pressure sensors and safety shut-offs to make sure they're working perfectly.
- Leak Detection: Using specialized tools, they'll perform a professional sweep for any potential leaks at the system's connections.
This mix of your own watchfulness and a yearly professional check-up is the key to keeping your CNG home fueling station in top shape. It’s what ensures you have a reliable—and completely secure—source of clean fuel right in your garage.
Your Top Questions About Home CNG Fueling, Answered
Alright, so you’ve learned how a CNG home fueling station works, run the numbers on cost, and gotten comfortable with the safety side of things. But you probably still have a few practical questions bouncing around in your head. That's a good thing—it means you're taking this seriously.
Let's dig into the common, real-world questions we hear from people just like you. These are the details that can make or break the decision to bring this technology home.
Can Any Car Be Converted to Run on CNG?
The short answer is no, but a whole lot of vehicles are great candidates. Honestly, the best fits are usually trucks, vans, and SUVs—vehicles with bigger, thirstier gasoline engines. The more fuel a vehicle burns, the faster you'll see a return on your investment from what you save on gas.
But it’s not just about engine size; the specific engine matters. The conversion itself involves adding a separate, high-pressure fuel system with a certified kit.
- A Pro Needs to Weigh In: The first step is always to have a certified CNG conversion tech look at your vehicle. They'll confirm your specific make, model, and year can be fitted with a compatible, EPA-approved kit.
- Small Engines Don't Always Pencil Out: For a car with a small, super-efficient engine, the fuel savings might not be enough to justify the $10,000+ price tag of a top-notch conversion.
- Dedicated or Bi-Fuel? You get to choose. A "dedicated" system runs only on CNG. A "bi-fuel" system, on the other hand, lets you switch between CNG and gasoline with the flip of a button, which is perfect for long trips where you might not find a public CNG station.
How Long Does It Really Take to Fill Up?
With a slow-fill home system, the mindset is "set it and forget it." To take a typical car from empty to full, you’re looking at anywhere from 6 to 10 hours. That sounds like a long time, but it’s designed to fit seamlessly into your life.
Think of it just like charging your phone. You plug it in when you go to bed and wake up with a full battery. It’s the same idea here—you connect the hose when you pull into the garage for the night, and by morning, your car is full and ready to go. The system is smart, too; it automatically shuts off once the tank hits its target pressure of 3,600 psi, so you don't have to babysit it.
Will My Utility Bills Go Through the Roof?
You’ll definitely see your natural gas and electricity bills go up. But don't let that scare you; you have to look at the bigger picture. Of course your gas bill will rise—you're now using it to fuel your car. Your electric bill will also tick up a bit to power the compressor.
The number that truly matters isn't the increase in your utility bills, but your net savings after you stop buying gasoline. That extra spend on gas and electricity is almost always just a fraction of what you were shelling out at the pump.
Let's say you save $200 a month on gasoline, but your combined utility bills go up by $40. You're still $160 ahead. Your total monthly energy spending drops, even though two individual bills went up.
Is the Compressor Loud When It's Running?
This is a great question, especially if you’re thinking of putting the unit in an attached garage or somewhere close to your neighbor's house. Most people say the noise from a home compressor is about the same as a modern, high-efficiency air conditioner or even a dishwasher.
It’s not dead silent, but it’s usually a low, steady hum that fades into the background. Manufacturers have gotten really good at sound-dampening, using insulated casings and mounts that absorb vibration. If you’re still concerned, here are a few smart moves:
- Ask for a Demo: See if your installer has a unit nearby that you can actually go listen to. Hearing it in person is the best way to know for sure.
- Check the Decibel Rating: The manufacturer’s spec sheet will list a decibel (dB) rating. You can look up what that number compares to in everyday sounds.
- Think About Placement: Installing the unit on a solid concrete pad and keeping it away from bedroom walls is a simple way to minimize any noise you might hear inside.
Getting these last few questions sorted out gives you a complete, practical understanding of what it’s really like to live with a CNG home fueling station—from the wallet to the daily routine.
At Blue Gas Express, we understand that permanent natural gas infrastructure isn't always an immediate option. For construction projects, utility interruptions, or any temporary need, our mobile CNG and LNG solutions provide the reliable energy you need, right when you need it. Discover how we can keep your project on track.