When we talk about an analysis of natural gas, we're doing more than just a routine check. We’re essentially creating a detailed chemical fingerprint of the fuel to make sure it’s safe, clean, and compatible with the equipment it’s meant to power. For anyone relying on temporary gas for construction or industrial work, this isn't just a technical step—it's a critical project management tool.
Why Natural Gas Analysis Is Critical for Project Success
Picture this: a multi-million dollar construction project suddenly grinds to a halt. It’s not a supply chain issue or a labor shortage. The culprit is something much more subtle—the temporary natural gas supply isn't compatible with the on-site generators. This isn't a hypothetical scenario; it's a costly reality for projects that overlook a proper analysis of natural gas.
This guide is designed to shift your perspective on gas analysis from a niche technical task to a core part of successful project management. The most important thing to remember is simple but crucial: not all natural gas is created equal. Its chemical makeup can vary wildly depending on its source, which directly impacts everything from equipment performance and safety to regulatory compliance.

The Growing Need for Diligent Analysis
The need for precise gas analysis is more urgent than ever. In 2025, the United States is poised to break records in both natural gas production and demand, putting a serious strain on our existing infrastructure. The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) projects that dry natural gas production will climb to a record 107.7 billion cubic feet per day (bcfd) in 2025.
This massive surge is fueling a $50 billion investment in new pipeline capacity, but construction just can't keep up. For builders in high-growth areas like North Carolina and Virginia, this often translates into long, frustrating delays for permanent gas lines. That’s where reliable temporary solutions become absolutely essential to keep projects on track. You can discover more about these energy market trends and their impact on oilprice.com.
Think of a detailed gas analysis report as an insurance policy. It prevents costly equipment damage, helps you avoid failed inspections, and guarantees the temporary fuel is a perfect match for the permanent supply that will eventually be connected.
Knowing the exact specifics of your gas supply is non-negotiable for keeping a project on schedule, within budget, and—most importantly—safe. When you properly analyze the gas, you ensure that temporary solutions like compressed natural gas (CNG) or liquefied natural gas (LNG) will integrate seamlessly with your operations.
Taking this proactive step empowers you to:
- Prevent Delays: Avoid failed commissioning tests or permit denials that stem from using an incompatible fuel.
- Protect Equipment: Make sure the gas quality meets the manufacturer’s specifications for your generators, boilers, and heaters.
- Maintain Safety: Identify and manage risks from contaminants or inconsistent fuel quality before they become a problem.
What's Actually in Your Natural Gas?
Think of a gas analysis report like a recipe card for your energy supply. It doesn't just say "natural gas"; it gives you the exact list of ingredients and their proportions. Understanding this breakdown is the only way to know precisely what you're feeding your expensive equipment.
The mix itself isn't terribly complicated. Natural gas is mostly a blend of hydrocarbons—molecules made of hydrogen and carbon—plus a few non-combustible gases that are just along for the ride. Let's look at the key players you'll see on every report.
The Good Stuff: Methane and Other Hydrocarbons
The undisputed star of the show is methane (CH4). It's the simplest and lightest hydrocarbon, and it usually makes up 80% to 95% of the total volume. Methane is what delivers the energy—when it burns, it creates the heat that fires up generators, warms buildings, and drives industrial processes. The more methane, the cleaner and more predictable the burn.
But methane rarely travels alone. It’s almost always mixed with a supporting cast of heavier hydrocarbons, often called Natural Gas Liquids (NGLs). These include:
- Ethane (C2H6): The second-most-common hydrocarbon. It’s often extracted and used to make plastics.
- Propane (C3H8): You know this one from your backyard grill. It's much more energy-dense than methane.
- Butane (C4H10): Even heavier than propane, butane is often blended into gasoline or sold as lighter fluid.
You can think of these heavier hydrocarbons as energy boosters. While methane provides the base load of energy, ethane, propane, and butane pack a bigger punch, driving up the gas's total heating value. A "rich" gas loaded with these NGLs delivers more energy per cubic foot, but it might require different equipment settings than a "lean" gas that's nearly pure methane. It’s a critical distinction.
The Fillers: Inert and Undesirable Gases
Not everything in the pipeline is fuel. The gas mixture also contains non-combustible components that contribute zero energy. They're essentially fillers that dilute the good stuff.
The most common ones you’ll see are:
- Nitrogen (N2): This is the main freeloader. While it's harmless, high levels of nitrogen water down the fuel's potency, forcing your equipment to burn more gas to get the same job done.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): Another non-combustible gas. Besides diluting the fuel, CO2 can become corrosive when it meets water, creating a long-term risk for pipelines and equipment internals.
It's like getting a watered-down drink. The more inert gases you have, the weaker the final product. For example, a gas analysis report showing 5% nitrogen means that for every 100 cubic feet of gas you pay for, only 95 cubic feet are actually doing any work. This directly hits your efficiency and your wallet, making it a crucial detail to watch.
Understanding Critical Gas Quality Metrics
So, we’ve covered the basic ingredients of natural gas. Now, let’s get into what really matters on the job site: how the quality of that gas mixture is measured. A proper analysis of natural gas is what translates those chemical components into practical numbers that tell you if your fuel is actually up to snuff.
Think of these metrics as the vital signs for your gas supply. They're the difference between a smooth project and a costly shutdown. We'll use a few simple analogies to break down these technical concepts, connecting each one back to real-world risks like equipment failure or a denied permit.
Measuring Heating Power With BTU Content
The most fundamental metric is the British Thermal Unit (BTU) content. This is basically the gas’s "calorie count"—it tells you exactly how much heat energy you get when you burn a specific amount of gas. It's a direct measure of its power.
A higher BTU value means the gas is more energy-dense, which usually points to a richer mix of heavier hydrocarbons like ethane and propane. On the flip side, a lower BTU value signals a "leaner" gas, one that's mostly methane or has non-combustible fillers like nitrogen just taking up space. Utilities have strict BTU ranges for their systems, and all your equipment is calibrated to expect a certain value. Feeding it gas outside that range is a recipe for poor performance or even serious damage.
This flowchart breaks down the key components that add up to the final BTU value and overall quality.
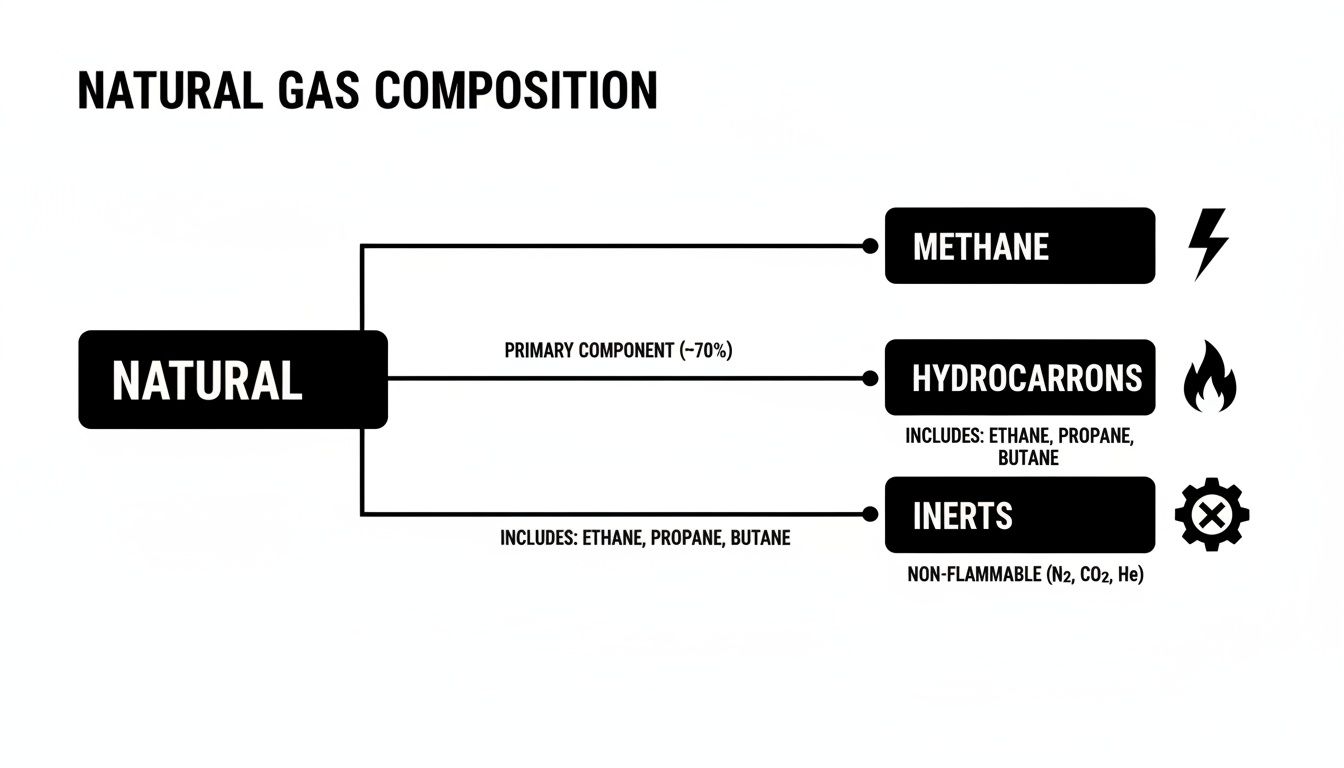
As you can see, it's the energy-producing hydrocarbons that do all the work. The inert gases are just along for the ride and dilute the fuel's power.
Ensuring Compatibility With The Wobbe Index
Next up is the Wobbe Index, and if you're using temporary gas services, this is arguably the most important number on the report. The Wobbe Index is essentially a "compatibility score." It confirms that your temporary gas supply will deliver the same amount of energy through an appliance's orifice as the permanent pipeline gas will.
This is all about interchangeability. If the Wobbe Index of your temporary CNG or LNG supply is a perfect match for the local utility's gas, your equipment—whether it's a furnace, boiler, or generator—won't even know the difference. It'll just work, operating safely and efficiently without any tweaks or adjustments. This is how you prevent those frustrating, and expensive, commissioning failures.
Key Takeaway: A matched Wobbe Index is non-negotiable. It’s the single best indicator that a temporary fuel source will behave identically to the permanent supply, ensuring seamless operational continuity for your project.
Protecting Engines With The Methane Number
If your project involves natural gas engines—think large-scale generators or co-gen plants—then the Methane Number (MN) is absolutely critical. You can think of it as the octane rating for natural gas. It measures the fuel’s ability to resist "knocking" or pre-ignition, a destructive event where the gas ignites on its own before the spark plug even fires.
A higher Methane Number means the gas is more stable and resistant to knocking, which is exactly what you need for high-compression engines. Using a gas with an MN that's too low can cause severe engine damage, leading to massive repair bills and crippling downtime. An accurate gas analysis is the only way to be certain the MN is right for your specific equipment.
Spotting Hidden Dangers and Contaminants
Finally, a comprehensive analysis screens for unwanted guests that can cause all sorts of headaches. The main culprits include:
- Hydrogen Sulfide (H₂S): This corrosive compound smells like rotten eggs for a reason—it eats away at pipes and equipment from the inside out. Most pipelines have a zero-tolerance policy for H₂S.
- Water Vapor (H₂O): Too much moisture is a huge problem. In cold weather, it can freeze and form ice plugs (known as hydrates) that block fuel lines and regulators, starving your equipment of fuel right when you need it most.
- Oxygen (O₂): While not damaging on its own, the presence of oxygen where it shouldn't be can signal a leak or other pipeline integrity issue, creating a major safety risk.
To give you a better sense of how these metrics fit together, here’s a quick-reference table that summarizes what they measure and why they’re so important for your projects.
Key Natural Gas Quality Parameters and Their Impact
| Metric | What It Measures | Why It's Critical for Your Project |
|---|---|---|
| BTU Content | The energy density or "heating power" of the gas. | Ensures equipment runs efficiently and meets performance specs. A mismatch can lead to underperformance or damage. |
| Wobbe Index | The interchangeability of different gas sources. | Guarantees a temporary supply (CNG/LNG) will behave exactly like the permanent utility gas, preventing operational failures. |
| Methane Number | The gas's resistance to engine "knocking." | Protects natural gas engines from catastrophic damage caused by pre-ignition. Essential for generators and heavy machinery. |
| Contaminants | The presence of harmful substances like H₂S, water, and O₂. | Prevents corrosion, freeze-ups, and dangerous safety hazards that can halt your project and cause costly repairs. |
Understanding these parameters is more important than ever.
The entire U.S. natural gas sector is seeing explosive growth in LNG exports, with projections showing a jump from 11.9 bcfd in 2024 to 14.9 bcfd in 2025. This record-setting pace is straining domestic infrastructure, often delaying permanent utility hookups for new construction and industrial facilities, especially in states like Tennessee and South Carolina. You can learn more about these 2025 energy production records and see how they impact local project timelines.
In these situations, mobile gas providers become indispensable. By using precise gas analysis, we can deploy compatible CNG or LNG units that meet exact utility specifications, allowing projects to move forward with commissioning and get the permits they need without waiting.
How to Read and Interpret a Gas Analysis Report
At first glance, a gas analysis report can look like a page of incomprehensible jargon. It's just a wall of chemical formulas, columns of numbers, and technical terms. But learning to decipher it is simpler than you think, and it’s the key to turning that document into a powerful decision-making tool.
Think of it as a pre-flight checklist for your project. A quick, methodical review helps you spot trouble before it leads to expensive delays or, worse, damaged equipment. Let's walk through how to read these reports so your temporary gas supply is a perfect match for your project's needs.
Locating the Key Data Points
When you open a gas analysis report, your eyes will naturally land on a table listing all the different chemical components. This is the heart of the report. The first thing you want to find is the mole percentage (Mol %) for each gas. This number tells you exactly how much of each component is in the mix.
Break it down into three main categories:
- The Main Fuel (Methane): Find Methane (CH4) on the list. This should be the biggest number you see, usually somewhere between 85% and 95%. This is what's actually doing the work.
- The Energy Boosters (NGLs): Now, look for Ethane (C2H6), Propane (C3H8), and Butanes (C4H10). These are heavier hydrocarbons that pack more of a punch and increase the gas's total energy content.
- The Inert Fillers: Finally, locate Nitrogen (N2) and Carbon Dioxide (CO2). These are non-combustible gases that essentially dilute the fuel, taking up space without adding any energy.
Once you’ve got a handle on those percentages, you can move on to the calculated values that really dictate performance in the real world. These are typically summarized in a separate section. You're looking for the BTU content, the Wobbe Index, and the relative density (sometimes called specific gravity).
Actionable Advice: The very first thing I always check is the BTU value. Compare it directly against the local utility's required range. This single number is often the main gatekeeper for whether the fuel will be accepted, and it can tell you instantly if you're on the right track.
A Red Flag Checklist for Quick Review
You don't need to scrutinize every single number on the report. By zeroing in on a few critical metrics, you can quickly spot potential deal-breakers. Use this checklist to catch common red flags that signal an incompatible or downright problematic gas supply.
A quick scan for these issues can save you from a world of hurt:
- High Nitrogen or CO2: Are the combined inert gases creeping above 4-5%? High levels mean you’re paying for filler that doesn’t burn, which can tank equipment efficiency and performance.
- Presence of Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S): This is a complete non-starter. Most systems require zero H2S. Even tiny, trace amounts are incredibly corrosive and will chew through pipes and equipment.
- Excessive Water Content: Is the water vapor level higher than the utility’s spec? This is typically around 7 lbs/MMCF (pounds per million cubic feet). Too much moisture can freeze up in regulators and create blockages, especially when the temperature drops.
- Wobbe Index Mismatch: Does the Wobbe Index fall outside the acceptable range provided by the utility? If it doesn’t match, the temporary gas won't burn the same way as the permanent supply, which is a surefire way to fail commissioning tests.
This systematic approach is more important than ever. The global demand for natural gas saw only moderate growth in 2025, rising by just 0.5% in the first three quarters across key markets. This slowdown was driven by high prices and economic headwinds, but it also underscores the growing need for flexible, reliable energy solutions. For builders and utilities here in the U.S. Southeast, these market shifts can mean a higher risk of maintenance outages and installation delays, making a dependable temporary gas partner absolutely essential. You can read the full research about these global gas market dynamics for more context.
By mastering the ability to read a gas analysis report, you’re no longer just a passive customer. You become an active partner in ensuring your project runs smoothly, protecting valuable assets, and keeping your timeline and budget firmly on track.
Keeping Your Project on Track When the Gas Isn't
Knowing the science behind gas analysis is great, but what really counts is putting that knowledge to work to keep a multi-million-dollar project from grinding to a halt. When the permanent gas line is delayed, your whole schedule is on the line. This is where a practical, precise analysis of natural gas is the only thing standing between a costly shutdown and a project that keeps moving forward.
The real challenge? Making sure a temporary fuel supply—like compressed natural gas (CNG) or liquefied natural gas (LNG)—acts as a perfect stand-in for the permanent utility gas. It's not good enough for the gas to just burn. It has to be an identical twin to the pipeline gas so that every single piece of equipment, from boilers to generators, runs perfectly without needing a single tweak. Get this right, and you avoid failed inspections, damaged equipment, and delays that bleed money.

How We Guarantee a Perfect Match
At Blue Gas Express, we’ve built a meticulous process to take all the guesswork out of fuel compatibility. It’s a systematic approach, driven by hard data and precision, to ensure our temporary supply is a perfect match for the utility’s, every single time. We don't just deliver gas; we deliver certainty.
Here’s how our process works:
- Get the Utility's Playbook: First things first, we get our hands on the official gas tariff sheet directly from the local utility. This document is the bible—it lays out the exact quality specifications for gas on their system, including the required BTU content and Wobbe Index range.
- Source the Right Stuff: With those specs as our guide, our team sources CNG or LNG that perfectly mirrors the utility’s profile. We then run our own comprehensive analysis on that temporary supply to confirm its composition and quality metrics before it even thinks about leaving our facility.
- Create a "Digital Twin" Fuel: The end result is a temporary fuel supply that is, for all intents and purposes, a "digital twin" of the permanent pipeline gas. This obsessive matching means that when our mobile units connect to your site, the transition is absolutely seamless.
This process flat-out eliminates the risk of incompatibility. Your equipment runs exactly as it should, your inspections pass without a problem, and your project stays on schedule.
Turning a Crisis into a Non-Issue
Think about a real-world mess we handled recently. A large commercial builder in North Carolina was just weeks from commissioning a huge new facility. Suddenly, they get the news: a six-month delay on their permanent gas line. This kind of setback can torpedo an entire schedule, stop them from getting their certificate of occupancy, and cost them thousands of dollars a day.
Case Study: A major commercial project faced a six-month utility delay, jeopardizing its occupancy permit. By providing a temporary CNG supply precisely matched to the local utility's gas tariff, Blue Gas Express enabled the builder to complete equipment commissioning and pass all inspections, keeping the project on schedule and avoiding costly penalties.
We were able to jump in immediately. After getting the local utility’s tariff sheet, we sourced and delivered a CNG supply with a Wobbe Index and BTU value that were a 99.8% match to their specs. Our solution turned a potential months-long catastrophe into a simple logistical step.
The builder fired up their HVAC systems and backup generators, passed their final inspections, and got their permit right on time. Our hands-on expertise in the analysis of natural gas was the key that kept their project moving.
Your Questions About Natural Gas Analysis, Answered
Even when you've got a handle on the science, practical questions always pop up on the job site. Project managers and builders often ask us how natural gas analysis actually affects their project timelines. Here are the straight answers to the most common questions we get.
How Often Should I Get a Gas Analysis?
Every single time. You need a new analysis for each distinct fuel delivery or source. Natural gas isn't a uniform product; its makeup can change quite a bit from one supplier to the next, or even from different wells owned by the same company.
For any temporary CNG or LNG job, a current, certified report is an absolute must-have before a single truck arrives on your site. This is your guarantee that the gas being delivered today meets the utility's specs and won't cause problems for your equipment.
Think of it like this: you wouldn't accept a concrete delivery without checking the slump test results against your engineering specs. Your fuel supply deserves the same level of scrutiny. It's the only way to head off expensive performance headaches.
What's the Single Most Important Number to Look At?
When you're using temporary fuel to bridge a utility gap, the Wobbe Index is king. Don't get me wrong, BTU content is important for energy output, but the Wobbe Index is the definitive measure of whether one gas can be swapped for another.
A perfectly matched Wobbe Index means your temporary supply will behave exactly like the permanent pipeline gas. This ensures every piece of equipment you have—from sensitive backup generators to massive heating systems—will run safely and efficiently without needing adjustments. It practically eliminates the risk of a failed commissioning test.
What Happens If the Temporary Supply Doesn't Match?
Using the wrong gas blend is a recipe for a domino effect of costly problems. The most immediate risks are:
- Failed Inspections: If your temporary fuel doesn't meet the utility's or local inspector's requirements, your project will fail commissioning. That means delays in getting your certificate of occupancy.
- Equipment Damage: An incorrect gas composition can cause engine knocking, incomplete combustion in boilers, or even trip up sensors. This can lead to expensive repairs and potentially void your equipment warranties.
- Skyrocketing Costs: A lower BTU value or a high percentage of inert gases means you have to burn more fuel to get the same amount of energy. Your operational costs will go up, plain and simple.
How Long Does It Take to Get the Results?
The lab work itself is pretty fast—usually done within 24 to 48 hours. A technician runs a sample through a gas chromatograph, which separates and measures every component to create a detailed report.
But the real key isn't the lab turnaround time; it's building this step into your logistics from the start. A good partner will have this analysis done before the fuel is even scheduled for delivery, confirming it's a perfect match well in advance. This approach prevents last-minute scrambles and keeps your project on track. A proper analysis of natural gas is all about ensuring continuity.
When utility hookup delays put your project at risk, don't gamble on your fuel supply. Blue Gas Express delivers meticulously tested and perfectly matched temporary CNG and LNG solutions to keep you up and running. Keep your project on schedule by learning more about our services.